H-DL-Ala-DL-Ala-OH
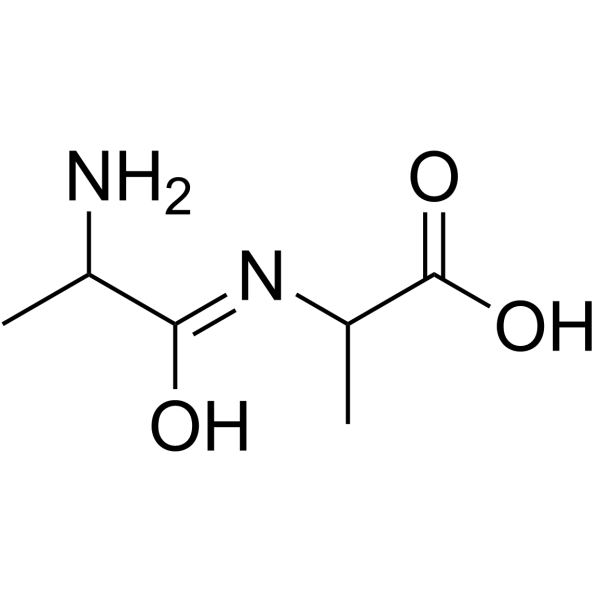
H-DL-Ala-DL-Ala-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-DL-Ala-DL-Ala-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2867-20-1 | Molecular Weight | 160.17100 | |
| Density | 1.208g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 402.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12N2O3 | Melting Point | 268-270ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 197.3ºC | |
|
Bond dissociation of the dipeptide dialanine and its derivative alanine anhydride induced by low energy electrons.
J. Chem. Phys. 134(5) , 054305, (2011) Dissociative electron attachment to dialanine and alanine anhydride has been studied in the gas phase utilizing a double focusing two sector field mass spectrometer. We show that low-energy electrons (i.e., electrons with kinetic energies from near zero up to... |
|
|
Infrared spectroscopy of the alanine dipeptide analog in liquid water with DFT-MD. Direct evidence for P(II)/beta conformations.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12 , 10198-10209, (2010) Following our previous work [J. Phys. Chem. B. Lett., 2009, 113, 10059], DFT-based molecular dynamics (DFTMD) simulations of 2-Ala peptide (i.e. Ac-Ala-NHMe dialanine peptide analog with methyl group caps at the extremities) immersed in liquid water at room t... |
|
|
Atomic multipoles: electrostatic potential fit, local reference axis systems, and conformational dependence.
J. Comput. Chem. 33(20) , 1673-88, (2012) Currently, all standard force fields for biomolecular simulations use point charges to model intermolecular electrostatic interactions. This is a fast and simple approach but has deficiencies when the electrostatic potential (ESP) is compared to that from ab ... |
|
|
Kinetic mechanism and inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis D-alanine:D-alanine ligase by the antibiotic D-cycloserine.
FEBS J. 280(4) , 1150-66, (2013) D-cycloserine (DCS) is an antibiotic that is currently used in second-line treatment of tuberculosis. DCS is a structural analogue of D-alanine, and targets two enzymes involved in the cytosolic stages of peptidoglycan synthesis: alanine racemase (Alr) and D-... |
|
|
Integrating diffusion maps with umbrella sampling: application to alanine dipeptide.
J. Chem. Phys. 134(13) , 135103, (2011) Nonlinear dimensionality reduction techniques can be applied to molecular simulation trajectories to systematically extract a small number of variables with which to parametrize the important dynamical motions of the system. For molecular systems exhibiting f... |
|
|
Toward canonical ensemble distribution from self-guided Langevin dynamics simulation.
J. Chem. Phys. 134(13) , 134108, (2011) This work derives a quantitative description of the conformational distribution in self-guided Langevin dynamics (SGLD) simulations. SGLD simulations employ guiding forces calculated from local average momentums to enhance low-frequency motion. This enhanceme... |
|
|
A fast parallel clustering algorithm for molecular simulation trajectories.
J. Comput. Chem. 34(2) , 95-104, (2013) We implemented a GPU-powered parallel k-centers algorithm to perform clustering on the conformations of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The algorithm is up to two orders of magnitude faster than the CPU implementation. We tested our algorithm on four pro... |
|
|
Umbrella integration with higher-order correction terms.
J. Chem. Phys. 136(23) , 234102, (2012) Umbrella integration is a method to analyze umbrella sampling simulations. It calculates free-energy changes from distributions obtained from molecular dynamics. While it can be formulated on the full sampled distributions, they are generally approximated by ... |
|
|
Dissociative electron attachment to glycyl-glycine, glycyl-alanine and alanyl-alanine.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(10) , 4600-6, (2011) The processes of negative ions formation of dipeptides glycyl-glycine, glycyl-alanine and alanyl-alanine in the conditions of resonant electron capture have been studied with a help of negative ions mass spectrometry. Using a thermochemical approach, the main... |
|
|
Fluoroolefins as peptide mimetics. 2. A computational study of the conformational ramifications of peptide bond replacement.
J. Phys. Chem. A 114(2) , 1123-33, (2010) The design of peptide mimetic compounds is greatly facilitated by the identification of functionalities that can act as peptide replacements. The fluoroalkene moiety has recently been employed for that purpose. The purpose of this work is to examine the confo... |