Elaidic Acid
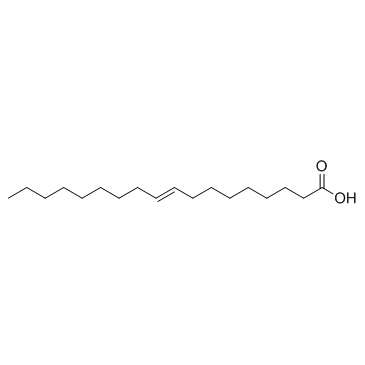
Elaidic Acid structure
|
Common Name | Elaidic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 112-79-8 | Molecular Weight | 282.461 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 360.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H34O2 | Melting Point | 42-44 ℃(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 270.1±14.4 °C | |
|
Development and application of a comparative fatty acid analysis method to investigate voriconazole-induced hepatotoxicity.
Clin. Chim. Acta 438 , 126-34, (2014) As fatty acids play an important role in biological regulation, the profiling of fatty acid expression has been used to discover various disease markers and to understand disease mechanisms. This study developed an effective and accurate comparative fatty aci... |
|
|
Influence of the sophorolipid molecular geometry on their self-assembled structures.
Chem. Asian J. 8(2) , 369-72, (2013)
|
|
|
Characterization of Shrimp Oil from Pandalus borealis by High Performance Liquid Chromatography and High Resolution Mass Spectrometry.
Mar. Drugs 13 , 3849-76, (2015) Northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis) oil, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, was recovered from the cooking water of shrimp processing facilities. The oil contains significant amounts of omega-3 fatty acids in triglyceride form, along with substantial long-... |
|
|
The Inhibitory Efficacy of Methylseleninic Acid Against Colon Cancer Xenografts in C57BL/6 Mice.
Nutr. Cancer 67 , 831-8, (2015) Data indicate that methylselenol is a critical selenium (Se) metabolite for anticancer activity in vivo. We tested the hypothesis that oral dosing methylseleninic acid (MSeA), a methylselenol precursor, inhibits the growth of colon cancer xenografts in C57BL/... |
|
|
Trans fatty acids exacerbate dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis by promoting the up-regulation of macrophage-derived proinflammatory cytokines involved in T helper 17 cell polarization.
Clin. Exp. Immunol. 174(3) , 459-71, (2013) Numerous reports have shown that a diet containing large amounts of trans fatty acids (TFAs) is a major risk factor for metabolic disorders. Although recent studies have shown that TFAs promote intestinal inflammation, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. I... |
|
|
Determination of elaidic and vaccenic acids in foods using GC × GC-FID and GC × GC-TOFMS
Talanta 85(1) , 252-8, (2011) Trans fatty acids (TFAs) are present in meat and dairy products as m ruminant animals and in vegetable fats due to partial hydrogenation. This study aimed to discriminate between natural (N-TFA) and hydrogenated trans fatty (H-TFA) acids by GC×GC-flame ioniza... |
|
|
Vaccenic and elaidic acid equally esterify into triacylglycerols, but differently into phospholipids of fed rat liver cells.
Lipids 46(7) , 647-57, (2011) Elaidic acid (trans-9-C₁₈:₁ or trans-9) is assumed to exert atherogenic effects due to its double bond configuration. The possibility that trans-9 and vaccenic acid (trans-11-C₁₈:₁ or trans-11), its positional isomer, were biochemically equivalent and interch... |
|
|
Deleterious impact of elaidic fatty acid on ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux from mouse and human macrophages.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1821(2) , 303-12, (2012) Consumption of trans fatty acids (TFA) increase cardiovascular risk more than do saturated FA, but the mechanisms explaining their atherogenicity are still unclear. We investigated the impact of membrane incorporation of TFA on cholesterol efflux by exposing ... |
|
|
Linolelaidic acid induces a stronger proliferative effect on human umbilical vein smooth muscle cells compared to elaidic acid.
Lipids 48(4) , 395-403, (2013) Trans fatty acids (TFA) have been considered as an independent risk factor of coronary heart disease, sudden death and insulin-resistance, and different TFA isomers may have different effects on the progression of cardiovascular diseases such as atheroscleros... |
|
|
Dietary trans fatty acids and composition of human atheromatous plaques.
Eur. J. Nutr. 43 , 313-318, (2004) Dietary fatty acids are incorporated into atheromatous plaques mainly in the form of cholesterol esters. Physicochemical properties of the plaque (e. g. mechanical strength) depend on its fatty acid composition. Trans isomers of unsaturated fatty acids (TFA) ... |