H-Arg-OEt·2HCl
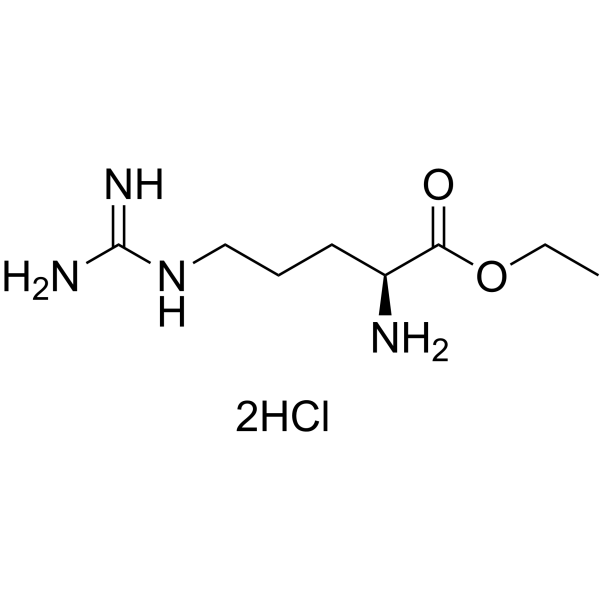
H-Arg-OEt·2HCl structure
|
Common Name | H-Arg-OEt·2HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 36589-29-4 | Molecular Weight | 275.176 | |
| Density | 1.26g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 343.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H20Cl2N4O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 161.4ºC | |
|
Intracellular l-arginine concentration does not determine NO production in endothelial cells: Implications on the “l-arginine paradox”
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 414 , 660-663, (2011) Highlights ► Our findings provide a possible solution to the “l-arginine paradox”. ► Extracellular l-arginine concentration is the major determinant of NO production. ► Cellular l-arginine action is limited by cellular ARG transport, not the Km of NOS. ► We e... |
|
|
L-arginine and arginine ethyl ester enhance proliferation of endothelial cells and preadipocytes - how an arginine ethyl ester-releasing biomaterial could support endothelial cell growth in tissue engineering.
Biomed Mater Eng 25 , 289-97, (2015) Adipose tissue engineering is a promising solution for the reconstruction of soft tissue defects. An insufficient neovascularisation within the scaffolds that leads to necrosis and tissue loss is still a major shortcoming of current tissue engineering attempt... |
Journals:
More...