1-O-HEXADECYL-2-N-METHYLCARBAMYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
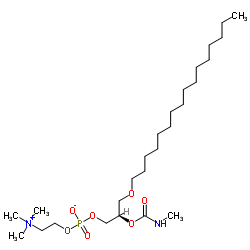
1-O-HEXADECYL-2-N-METHYLCARBAMYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE structure
|
Common Name | 1-O-HEXADECYL-2-N-METHYLCARBAMYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91575-58-5 | Molecular Weight | 538.698 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H55N2O7P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid inhibits delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions via the platelet-activating factor receptor.
J. Clin. Invest. 115(10) , 2855-61, (2005) Staphylococcus aureus infections are known triggers for skin inflammation and can modulate immune responses. The present studies used model systems consisting of platelet-activating factor receptor-positive and -negative (PAF-R-positive and -negative) cells a... |
|
|
Platelet-activating factor biosynthesis induced by various stimuli in human HaCaT keratinocytes.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 107(1) , 88-94, (1996) Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a potent inflammatory mediator that is thought to play a role in cutaneous inflammation. These studies used mass spectrometry to examine the molecular species of PAF precursor glycerophosphocholine lipids (GPC) as well as t... |
|
|
The secreted protease factor CPAF is responsible for degrading pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(42) , 31495-501, (2006) Chlamydia trachomatis has evolved a profound anti-apoptotic activity that may aid in chlamydial evasion of host defense. The C. trachomatis anti-apoptotic activity has been correlated with blockade of mitochondrial cytochrome c release, inhibition of Bax and ... |
|
|
Evidence for involvement of the epidermal platelet-activating factor receptor in ultraviolet-B-radiation-induced interleukin-8 production.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 115(2) , 267-72, (2000) Ultraviolet B radiation has been shown to generate cutaneous inflammation in part through inducing oxidative stress and cytokine production in human keratinocytes. Amongst the proinflammatory cytokines synthesized in response to ultraviolet B radiation is the... |
|
|
Platelet-activating factor induces collagenase expression in corneal epithelial cells.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90(18) , 8678-82, (1993) Platelet-activating factor (PAF), a potent lipid mediator involved in inflammatory and immune responses, accumulates rapidly in response to injury in a variety of tissues, including the corneal epithelium. However, the precise role of this compound in the cas... |
|
|
Activation of platelet-activating factor receptor in SZ95 sebocytes results in inflammatory cytokine and prostaglandin E2 production.
Exp. Dermatol. 15(10) , 769-74, (2006) Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a group of phosphocholines with various biological effects mediated by the PAF receptor (PAF-R). Activation of the epidermal PAF-R induces the expression of inflammatory mediators, including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and pro... |
|
|
Involvement of platelet-activating factor in ultraviolet B-induced hyperalgesia.
J. Invest. Dermatol. 129(1) , 167-74, (2009) Ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation causes cutaneous inflammation. One important clinical consequence of UVB-induced inflammation is increased pain or hyperalgesia, which is likely mediated by enhanced sensitivity of cutaneous sensory neurons. Previous studies have... |
|
|
Activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) by platelet activating factor mediates migration and cell death in cerebellar granule neurons.
Eur. J. Neurosci. 13(10) , 1913-22, (2001) Children with vertically acquired HIV-1 can present with a rapidly progressive encephalopathy and neuronal apoptosis in the first 12-18 months of life. Furthermore, abnormal prenatal platelet activating factor (PAF) signalling may result in lissencephaly, a d... |
|
|
Expression of the platelet-activating factor receptor results in enhanced ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis in a human epidermal cell line.
J. Biol. Chem. 273(30) , 18891-7, (1998) Recent studies have demonstrated that ultraviolet B radiation (UVB) damages human keratinocytes in part by inducing oxidative stress and cytokine production. Severe UVB damage to the keratinocyte can also result in apoptosis or programmed cell death. Although... |
|
|
Agonist-induced down-regulation of platelet-activating factor receptor gene expression in U937 cells.
Biochem. J. 301 ( Pt 3) , 911-6, (1994) Prolonged exposure (8-24 h) of human promonocytic U937 cells to 100 nM 1-O-hexadecyl-2-N-methylcarbamyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (carbarmyl-PAF), a non-metabolizable analogue of platelet-activating factor (PAF), reduced the numbers of PAF receptors by 50-7... |