Imazethapyr
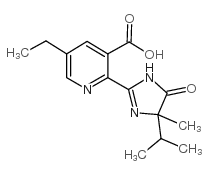
Imazethapyr structure
|
Common Name | Imazethapyr | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 81335-77-5 | Molecular Weight | 289.33000 | |
| Density | 1.28 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 446.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H19N3O3 | Melting Point | 169-173ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 224ºC | |
|
Enantioselective phytotoxicity of the herbicide imazethapyr and its effect on rice physiology and gene transcription.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(16) , 7036-43, (2011) Imazethapyr (IM) is a chiral herbicide and a widely used racemic mixture. This report investigated the enantioselectivity between R- and S-IM in rice and explored its causative mechanism at the physiological and molecular levels. The results suggested that R-... |
|
|
Molecular mechanism of enantioselective inhibition of acetolactate synthase by imazethapyr enantiomers.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(7) , 4202-6, (2010) Chiral compounds usually behave enantioselectively in phyto-biochemical processes. Imidazolinones are a class of chiral herbicides that are widely used. They inhibit branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis in plants by targeting acetolactate synthase (ALS). It... |
|
|
Enantioselective phytotoxicity of the herbicide imazethapyr on the response of the antioxidant system and starch metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana.
PLoS ONE 6(5) , e19451, (2011) The enantiomers of a chiral compound possess different biological activities, and one of the enantiomers usually shows a higher level of toxicity. Therefore, the exploration of the causative mechanism of enantioselective toxicity is regarded as one of primary... |
|
|
Abiotic degradation (photodegradation and hydrolysis) of imidazolinone herbicides.
J. Environ. Sci. Health B 43(2) , 105-12, (2008) The abiotic degradation of the imidazolinone herbicides imazapyr, imazethapyr and imazaquin was investigated under controlled conditions. Hydrolysis, where it occurred, and photodegradation both followed first-order kinetics for all herbicides. There was no h... |
|
|
Photodegradation of the herbicide imazethapyr in aqueous solution: effects of wavelength, pH, and natural organic matter (NOM) and analysis of photoproducts.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(13) , 7277-85, (2011) The photodegradation of imazethapyr, 5-ethyl-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydroimidazol-1H-3-yl)nicotinic acid, has been investigated in phosphate buffers and in buffered solutions containing natural organic matter (NOM). Imazethapyr degrades most quic... |
|
|
Unraveling the role of fermentation in the mode of action of acetolactate synthase inhibitors by metabolic profiling.
J. Plant Physiol. 168(13) , 1568-75, (2011) Herbicides that inhibit branched chain amino acid biosynthesis induce aerobic fermentation. The role of fermentation in the mode of action of these herbicides is not known, nor is the importance of this physiological response in the growth inhibition and the ... |
|
|
Sorption characteristics of atrazine and imazethapyr in soils of new zealand: importance of independently determined sorption data.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(22) , 10866-75, (2009) We investigated sorption characteristics of two commonly used herbicides, atrazine and imazethapyr, in 101 soils with allophanic and non-allophanic clays of New Zealand using the batch equilibration technique. Soil properties, such as organic carbon (OC) cont... |
|
|
Interaction between saflufenacil and imazethapyr in red rice (Oryza ssp.) and hemp sesbania (Sesbania exaltata) as affected by light intensity.
Pest Manag. Sci. 68(7) , 1010-8, (2012) Saflufenacil is a broadleaf herbicide for preplant burndown and pre-emergence applications in various crops. This study was established to evaluate the absorption and translocation of saflufenacil in hemp sesbania and imazethapyr in red rice as a function of ... |
|
|
Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) in vivo assay for screening imidazolinone-resistance in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).
Plant Physiol. Biochem. 61 , 103-7, (2012) The objective of this work was to evaluate the in vivo acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) activity response to imidazolinones and its possible use as a selection method for evaluating AHAS inhibitor resistance. In vivo AHAS assay and the comparison of parameter... |
|
|
Response of the soil microbial community to imazethapyr application in a soybean field.
J. Environ. Sci. Health B 48(6) , 505-11, (2013) The objective of this study was to determine the effects of imazethapyr on soil microbial communities combined with its effect on soybean growth. A short-term field experiment was conducted, and imazethapyr was applied to the soil at three different doses [1-... |