Elastin
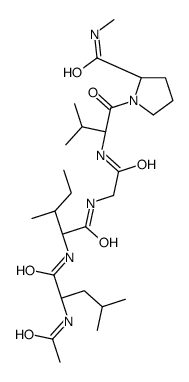
Elastin structure
|
Common Name | Elastin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9007-58-3 | Molecular Weight | 552.70700 | |
| Density | 1.126g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 916.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H48N6O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 508.2ºC | |
|
[Investigation of fluorescent components of drug "heparin" and its complexing with phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan].
Bioorg. Khim. 39(1) , 55-60, (2013) Using spectral-luminescent and spectrophotometric methods a composition of aminoacidic (AA) and protein components of commercial drug of heparin (Hep) as well as its interaction with Trp, Tyr and Phe was studied. The impurities of aromatic aminoacids Phe, Tyr... |
|
|
Elastin-derived peptides are new regulators of insulin resistance development in mice.
Diabetes 62(11) , 3807-16, (2013) Although it has long been established that the extracellular matrix acts as a mechanical support, its degradation products, which mainly accumulate during aging, have also been demonstrated to play an important role in cell physiology and the development of c... |
|
|
Skin extracellular matrix stimulation following injection of a hyaluronic acid-based dermal filler in a rat model.
Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 134(6) , 1224-33, (2014) Hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers have gained rapid acceptance for treating facial wrinkles and deep tissue folds. Although their space-filling properties are well understood, this study evaluates the cellular and molecular changes in skin, as a secondary ... |
|
|
Enhanced caspase activity contributes to aortic wall remodeling and early aneurysm development in a murine model of Marfan syndrome.
Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 35(1) , 146-54, (2015) Rupture and dissection of aortic root aneurysms remain the leading causes of death in patients with the Marfan syndrome, a hereditary connective tissue disorder that affects 1 in 5000 individuals worldwide. In the present study, we use a Marfan mouse model (F... |
|
|
Chronic intrauterine pulmonary hypertension increases main pulmonary artery stiffness and adventitial remodeling in fetal sheep.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 307(11) , L822-8, (2014) Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) is a clinical syndrome that is characterized by high pulmonary vascular resistance due to changes in lung vascular growth, structure, and tone. PPHN has been primarily considered as a disease of the smal... |
|
|
A novel approach to reconstruct a large full thickness abdominal wall defect: successful treatment with MatriDerm® and Split.
J. Wound Care 23(7) , 355-7, (2014) Reconstruction of large abdominal wall defects is a challenging procedure, often contraindicated in critically ill patients, with high incidences of complications. We present a case of a patient with a large abdominal wall defect who had reconstruction with M... |
|
|
Function of latent TGFβ binding protein 4 and fibulin 5 in elastogenesis and lung development.
J. Cell Physiol. 230(1) , 226-36, (2015) Mice deficient in Latent TGFβ Binding Protein 4 (Ltbp4) display a defect in lung septation and elastogenesis. The lung septation defect is normalized by genetically decreasing TGFβ2 levels. However, the elastic fiber assembly is not improved in Tgfb2(-/-) ;Lt... |
|
|
Inhibition of elastin peptide-mediated angiogenic signaling mechanism(s) in choroidal endothelial cells by the α6(IV)NC1 collagen fragment.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54(13) , 7828-35, (2013) The inhibitory effects and mechanism(s) of type IV collagen α-6 chain-derived noncollagenous domain (α6[IV]NC1 or hexastatin) on elastin-derived peptide (EDP)-activated choroidal endothelial cell migration, kinase signaling, and membrane type 1 metalloprotein... |
|
|
[The role of electrothermoadhesion in creation of artificial vocal cord, and the voice quality improvement following chordectomy for laryngeal cancer].
Klin. Khir. (2) , 77, (2013)
|
|
|
Protocol for the preparation of stimuli-responsive gold nanoparticles capped with elastin-based pentapeptides.
Methods Mol. Biol. 991 , 353-62, (2013) Stimuli-responsive materials are playing an increasingly important role in a wide range of applications such as drug delivery, diagnostics, sensors, and tissue engineering. Among them, gold nanoparticles responding to changes in their surrounding environment ... |