(D-Ala2,N-Me-Phe4,glycinol5)-Enkephalin acetate salt
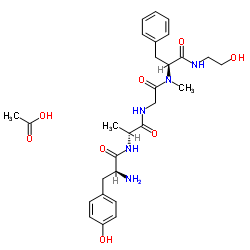
(D-Ala2,N-Me-Phe4,glycinol5)-Enkephalin acetate salt structure
|
Common Name | (D-Ala2,N-Me-Phe4,glycinol5)-Enkephalin acetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 100929-53-1 | Molecular Weight | 573.638 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 922.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H39N5O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 511.8ºC | |
|
Buprenorphine decreases the CCL2-mediated chemotactic response of monocytes.
J. Immunol. 194(7) , 3246-58, (2015) Despite successful combined antiretroviral therapy, ∼ 60% of HIV-infected people exhibit HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). CCL2 is elevated in the CNS of infected people with HAND and mediates monocyte influx into the CNS, which is critical in n... |
|
|
Morphine-induced internalization of the L83I mutant of the rat μ-opioid receptor.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(2) , 593-605, (2014) Naturally occurring single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within GPCRs can result in alterations in various pharmacological parameters. Understanding the regulation and function of endocytic trafficking of the μ-opioid receptor (MOP receptor) is of great imp... |
|
|
Microglia disrupt mesolimbic reward circuitry in chronic pain.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 8442-50, (2015) Chronic pain attenuates midbrain dopamine (DA) transmission, as evidenced by a decrease in opioid-evoked DA release in the ventral striatum, suggesting that the occurrence of chronic pain impairs reward-related behaviors. However, mechanisms by which pain mod... |
|
|
The contribution of Gi/o protein to opioid antinociception in an oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy rat model.
J. Pharmacol. Sci. 126(3) , 264-73, (2014) Oxaliplatin is a chemotherapeutic agent that induces chronic refractory neuropathy. To determine whether opioids effectively relieve this chronic neuropathy, we investigated the efficacies of morphine, oxycodone, and fentanyl, and the mechanisms underlying op... |
|
|
Activation of mu or delta opioid receptors in the lumbosacral spinal cord is essential for ejaculatory reflexes in male rats.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0121130, (2015) Ejaculation is controlled by a spinal ejaculation generator located in the lumbosacral spinal cord, consisting in male rats of lumbar spinothalamic (LSt) cells and their inter-spinal projections to autonomic and motor centers. LSt cells co-express several neu... |
|
|
Effect of μ-opioid agonist DAMGO on surface CXCR4 and HIV-1 replication in TF-1 human bone marrow progenitor cells.
BMC Res. Notes 7 , 752, (2014) Approximately one-third of the AIDS cases in the United States have been attributed to the use of injected drugs, frequently involving the abuse of opioids. Consequently, it is critical to address whether opioid use directly contributes to altered susceptibil... |
|
|
Single-Molecule Imaging of PSD-95 mRNA Translation in Dendrites and Its Dysregulation in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 7116-30, (2015) Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is caused by the loss of the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), an RNA binding protein that regulates translation of numerous target mRNAs, some of which are dendritically localized. Our previous biochemical studies using sy... |
|
|
Role of Phosphorylation Sites in Desensitization of µ-Opioid Receptor.
Mol. Pharmacol. 88 , 825-35, (2015) Phosphorylation of residues in the C-terminal tail of the µ-opioid receptor (MOPr) is thought to be a key step in desensitization and internalization. Phosphorylation of C-terminal S/T residues is required for internalization (Just et al., 2013), but its role... |
|
|
A heroin addiction severity-associated intronic single nucleotide polymorphism modulates alternative pre-mRNA splicing of the μ opioid receptor gene OPRM1 via hnRNPH interactions.
J. Neurosci. 34(33) , 11048-66, (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the OPRM1 gene have been associated with vulnerability to opioid dependence. The current study identifies an association of an intronic SNP (rs9479757) with the severity of heroin addiction among Han-Chinese male hero... |
|
|
Inhibition of opioid receptor mediated G-protein activity after chronic administration of kynurenic acid and its derivative without direct binding to opioid receptors.
CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 13(9) , 1520-9, (2014) There is an increasing number of evidence showing analgesic properties of the kynurenic acid (KYNA), and also some studies demonstrate that kynurenine might interact with the opioid system. Therefore in this study, for the first time we investigated the direc... |