6-nitrobenz(a)pyrene
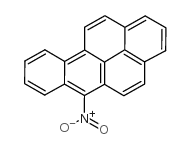
6-nitrobenz(a)pyrene structure
|
Common Name | 6-nitrobenz(a)pyrene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 63041-90-7 | Molecular Weight | 297.30700 | |
| Density | 1.429g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 524.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H11NO2 | Melting Point | 255.5°C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 259.5ºC | |
|
Comparative lung tumorigenicity of parent and mononitro-polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in the BLU:Ha newborn mouse assay.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 99(3) , 555-63, (1989) A BLU:Ha newborn mouse lung adenoma bioassay was employed to compare the tumorigenicity of selected mononitroarenes and unsubstituted parent compounds 6 months after initial treatment. The presence of a nitro group had a variable effect upon compound potency ... |
|
|
Metabolism of isomeric nitrobenzo[a]pyrenes leading to DNA adducts and mutagenesis.
Mutat. Res. 376(1-2) , 43-51, (1997) We have been interested in determining the structural and electronic features that may be useful in predicting the mutagenic activity of nitro-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (nitro-PAHs). We have previously found that a correlation between structural and el... |
|
|
Structure and vibrational spectra of mononitrated benzo[a]pyrenes.
J. Phys. Chem. A 110(1) , 76-84, (2006) The molecules benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) and 1-, 3-, and 6-nitrobenzo[a]pyrene (1-NBaP, 3-NBaP, 6-NBaP) are currently of significant interest due to their presence in respirable combustion exhaust particulates and their mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. Struct... |
|
|
Mutagenicity of the mononitrobenzo[a]pyrenes in Chinese hamster ovary cells mediated by rat hepatocytes or liver S9.
Carcinogenesis 7(4) , 681-4, (1986) Previous studies have shown that 1- and 3-nitrobenzo[a]pyrene (NBaP) were mutagenic in the Salmonella reversion assay without exogenous activation and that 1-, 3- and 6-NBaP were mutagenic in the presence of hepatocytes or liver homogenate (S9). In the presen... |
|
|
Transforming activity of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their nitro-derivatives in BALB/3T3 A31-1-1 cells.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 32(7) , 611-5, (1994) The transforming activities of four polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and six of their nitro-derivatives were studied using BALB/3T3 clone A31-1-1 cells in the absence of exogenous metabolic activation. Each compound was assayed two to four times to its maxima... |
|
|
Metabolism of 6-nitrochrysene by intestinal microflora.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54(1) , 197-203, (1988) Since bacterial nitroreduction may play a critical role in the activation of nitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, we have used batch and semicontinuous culture systems to determine the ability of intestinal microflora to metabolize the carcinogen 6-nitrochr... |
|
|
Ring oxidation of 6-nitrobenzo (a) pyrene by female mouse liver.
Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 58(1) , 63-74, (1987) 6-Nitrobenzo (a) pyrene (6-NBaP) is an environmental contaminant. In bacterial mutagenesis assays, 6-NBaP requires rat liver S9 enzymes for its activity. Chemical characterization of metabolites of 6-NBaP produced by male rat liver microsomes showed them to b... |
|
|
Chromatographic and spectral investigations on the in vivo metabolites of 6-nitrobenzo[a]pyrene.
J. Chromatogr. A. 450(3) , 325-36, (1988) 6-Nitrobenzo[a]pyrene (6-NBaP) occurs in the environment, is mutagenic in the Ames assay in the presence of added S9 and is carcinogenic to male but not female mouse liver when injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) into mice. In order to understand what kinds of ... |
|
|
Morphological transformation in three mammalian cell systems following treatment with 6-nitrochrysene and 6-nitrobenzo[a]pyrene.
Carcinogenesis 8(4) , 503-7, (1987) Two nitroaromatics, 6-nitrobenzo[a]pyrene (6-N-BaP) and 6-nitrochrysene (6-N-CRY), and the corresponding parent hydrocarbons, benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) and chrysene (CRY), were studied in in vitro transformation assays with Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cells, BALB/... |
|
|
Metabolism of 6-nitrobenzo[a]pyrene in rat lung preparations.
Toxicol. Lett. 37(3) , 229-33, (1987) 6-Nitrobenzo[alpha]pyrene (6-NBaP) occurs in our environment. Since human exposure to environmental contaminants may occur via the inhalation route, we examined the metabolites of 6-NBaP formed in lung preparations, and compared the metabolite profile to that... |