POLY(2-ETHYL-2-OXAZOLINE)
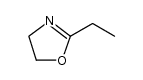
POLY(2-ETHYL-2-OXAZOLINE) structure
|
Common Name | POLY(2-ETHYL-2-OXAZOLINE) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 25805-17-8 | Molecular Weight | 99.13110 | |
| Density | 1.05 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 128.4ºCat 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | (C5H9NO)x | Melting Point | -62ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 29.4ºC | |
|
Polymeric micelles of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-block-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) copolymer as a carrier for paclitaxel.
J. Control. Release 89(3) , 437-46, (2003) Polymeric micelles based on amphiphilic block copolymers of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEtOz) and poly(epsilon -caprolactone) (PCL) were prepared in an aqueous phase. The loading of paclitaxel into PEtOz-PCL micelles was confirmed by 1H-NMR spectra. Paclitaxe... |
|
|
Polymeric micelles with a pH-responsive structure as intracellular drug carriers.
J. Control. Release 108(1) , 140-9, (2005) Polymeric micelles based on poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-b-poly(L-lactide) (PLLA-PEOz-PLLA) ABA triblock copolymers were designed as intracellular drug carriers. The PLLA-PEOz-PLLA micelles adopt a "flower-like" arrangement with A-blocks at the... |
|
|
Non-viral-mediated gene therapy approaches for bone repair.
Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 8(3) , 183-90, (2005) Bone repair strategies continue to be developed for alternatives to autografting, allogeneic implants of banked bone, and other bone substitutes. Efforts have included the delivery of potent growth and/or differentiation factors and the use of gene therapy. F... |
|
|
DNA transfection using linear poly(ethylenimine) prepared by controlled acid hydrolysis of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline).
J. Control. Release 73(2-3) , 391-9, (2001) A series of linear poly(ethylenimine) (L-PEI) containing varying amounts of cationic charge density in its backbone was produced by controlled hydrolysis of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEtOz) for using as a nonviral DNA transfection agent. The effects of catio... |
|
|
Electrically erodible polymer gel for controlled release of drugs.
Nature 354(6351) , 291-3, (1991) New controlled drug-delivery systems are being explored to overcome the disadvantages of conventional dosage forms. For example, stimulated drug-delivery has been used to overcome the tolerance problems that occur with a constant delivery rate, to mimic the p... |
|
|
Paclitaxel and iron oxide loaded multifunctional nanoparticles for chemotherapy, fluorescence properties, and magnetic resonance imaging.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 100(5) , 1279-92, (2012) The multifunctional nanoparticles constructed from triphenylamine-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-poly(ethyleneglycol)-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (TPA-PEP) and folate-poly(2-ethyl-2oxazoline)-poly(D,L-lactide) (folate-PEOz-PLA) were developed in this study. Iron o... |
|
|
Specific interactions study in complexes of poly(mono-n-alkyl itaconates) with tertiary polyamides.
Appl. Spectrosc. 57(7) , 829-34, (2003) This paper reports an FT-IR study of blends of poly(mono-n-alkyl itaconates) with poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMA) and poly(ethyloxazoline) (PEOX). Strong hydrogen bonding has been found, and both polybases have shown similar acceptor strengths. Derivative... |
|
|
New amphiphilic poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)/ poly(L-lactide) triblock copolymers.
Biomacromolecules 4(6) , 1487-90, (2003) A new series of cationic, thermo-sensitive, and biodegradable poly(L-lactide)-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-poly(L-lactide) (PLLA-PEOz-PLLA) triblock copolymers were synthesized by ring-opening polymerization. With increasing molecular weight and crystallinity of... |