Valerenic acid
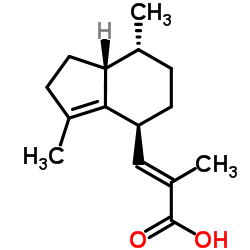
Valerenic acid structure
|
Common Name | Valerenic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3569-10-6 | Molecular Weight | 234.334 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 374.5±21.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H22O2 | Melting Point | 134-139ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 274.2±13.0 °C | |
|
Concise synthesis of Valerena-4,7(11)-diene, a highly active sedative, from valerenic acid.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 74(9) , 1963-4, (2010) A concise synthesis of valerena-4,7(11)-diene with potent sedative activity was achieved in three steps involving, reduction of carboxylic acid, bromination of the resulting alcohol, and reduction of the bromide from valerenic acid in a 63% total yield. This ... |
|
|
Root colonization by symbiotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increases sesquiterpenic acid concentrations in Valeriana officinalis L.
Planta Med. 76(4) , 393-8, (2010) In some medicinal plants a specific plant-fungus association, known as arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbiosis, increases the levels of secondary plant metabolites and/or plant growth. In this study, the effects of three different AM treatments on biomass and s... |
|
|
Valerian extract and valerenic acid are partial agonists of the 5-HT5a receptor in vitro.
Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 138(2) , 191-7, (2005) Insomnia is the most frequently encountered sleep complaint worldwide. While many prescription drugs are used to treat insomnia, extracts of valerian (Valeriana officinalis L., Valerianaceae) are also used for the treatment of insomnia and restlessness. To de... |
|
|
Valerian extract characterized by high valerenic acid and low acetoxy valerenic acid contents demonstrates anxiolytic activity.
Phytomedicine 19(13) , 1216-22, (2012) Valerian is one of the most commonly used herbal remedies for the treatment of insomnia and anxiety. Valerian extracts allosterically modulate GABAA receptors, an action related to valerenic acid, which is one of the active compounds determined from pharmacol... |
|
|
Chemical fingerprinting of valeriana species: simultaneous determination of valerenic acids, flavonoids, and phenylpropanoids using liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection.
J. AOAC Int. 89(1) , 8-15, (2006) The roots and rhizomes of various valeriana species are currently used as a sleeping aid or mild sedative. A liquid chromatography method has been developed that permits the analysis of chlorogenic acid, lignans, flavonoids, valerenic acids, and valpotrates i... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of valerenic acid after administration of valerian in healthy subjects.
Phytother Res. 19(9) , 801-3, (2005) To describe the pharmacokinetics of valerenic acid in a group of healthy adults after a single oral dose of valerian using a newly developed sensitive assay for serum concentrations of valerenic acid, a commonly used marker for qualitative and quantitative an... |
|
|
Effect of valerian, valerian/hops extracts, and valerenic acid on glucuronidation in vitro.
Xenobiotica 37(2) , 113-23, (2007) Valerian preparations alone or in combination with hops are popular over-the-counter products used for sleep disturbances or anxiety. Therefore, it is important to characterize the effect of these products on the activity of human drug-metabolizing enzymes. T... |
|
|
Anxiolytic properties of Valeriana officinalis in the zebrafish: a possible role for metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Planta Med. 78(16) , 1719-24, (2012) Valerian extract is used in complementary and alternative medicine for its anxiolytic and sedative properties. Our previous research demonstrated valerian interactions with glutamate receptors. The purpose of this study was to determine if valerian anxiolytic... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of valerenic acid after single and multiple doses of valerian in older women.
Phytother Res. 24(10) , 1442-6, (2010) Insomnia is a commonly reported clinical problem with as many as 50% of older adults reporting difficulty in falling and/or remaining asleep. Valerian (Valeriana officinalis) is a commonly used herb that has been advocated for promoting sleep. Valerenic acid ... |
|
|
Antioxidant effect and study of bioactive components of Valeriana sisymbriifolia and Nardostachys jatamansii in comparison to Valeriana officinalis.
Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 26(1) , 53-8, (2013) The roots of Nardostachys jatamansi have been used as a substitute for valerian in Iranian traditions. Moreover, six species from Valeriana genus such as V. sisymbriifolia grow in Iran which has not been studied yet. We aimed to study of antioxidant effect of... |