2-Azahypoxanthine
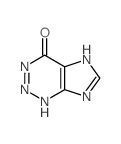
2-Azahypoxanthine structure
|
Common Name | 2-Azahypoxanthine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4656-86-4 | Molecular Weight | 137.10000 | |
| Density | 2.263g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 512.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H3N5O | Melting Point | 264 °C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 264ºC | |
|
Role of tautomerism of 2-azaadenine and 2-azahypoxanthine in substrate recognition by xanthine oxidase.
J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 11(2) , 153-62, (1997) The tautomerism of 2-azaadenine and 2-hypoxanthine has been examined in the gas phase and in aqueous solution. The tautomerism in the gas phase has been studied by means of semiempirical and ab initio quantum-mechanical computations, as well as density-functi... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of dacarbazine, its photolytic degradation product, 2-azahypoxanthine, and the metabolite 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide in plasma and urine by high-pressure liquid chromatography.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 27(6) , 977-9, (1985) A high-pressure liquid chromatographic method has been developed that allows for the simultaneous analysis of dacarbazine (DTIC), 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC), and 2-azahypoxanthine (2-AZA) in plasma or urine. Plasma samples were prepared by ultrafilt... |
|
|
Metabolism and metabolic effects of 2-azahypoxanthine and 2-azaadenosine.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 34(8) , 1293-304, (1985) The metabolism and metabolic effects of 2-azahypoxanthine and 2-azaadenosine were studied to elucidate the biochemical basis for their known cytotoxicities. 2-Azaadenosine is a known substrate for adenosine kinase. That 2-azahypoxanthine is a substrate for hy... |
|
|
Disclosure of the "fairy" of fairy-ring-forming fungus Lepista sordida.
ChemBioChem. 11(10) , 1373-7, (2010)
|
|
|
Mechanisms of 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno)imidazole-4-carboxamide (Dacarbazine) cytotoxicity toward Chinese hamster ovary cells in vitro are dictated by incubation conditions.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 58(3) , 319-31, (1986) Decomposition of the antitumor agent 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno)imidazole-4-carboxamide (DTIC, Dacarbazine) produces several potentially toxic compounds, the concentration of which depend on incubation parameters such as pH, temperature and illumination. The ... |