TAUROLITHOCHOLIC ACID SODIUM SALT
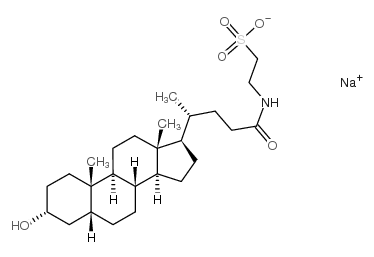
TAUROLITHOCHOLIC ACID SODIUM SALT structure
|
Common Name | TAUROLITHOCHOLIC ACID SODIUM SALT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6042-32-6 | Molecular Weight | 505.68600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H44NNaO5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Bile acid receptor TGR5 agonism induces NO production and reduces monocyte adhesion in vascular endothelial cells.
Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 33(7) , 1663-9, (2013) TGR5 is a G-protein-coupled receptor for bile acids. So far, little is known about the function of TGR5 in vascular endothelial cells.In bovine aortic endothelial cells, treatment with a bile acid having a high affinity to TGR5, taurolithocholic acid (TLCA), ... |
|
|
Angiotensin II protects primary rat hepatocytes against bile salt-induced apoptosis.
PLoS ONE 7(12) , e52647, (2012) Angiotensin II (AT-II) is a pro-fibrotic compound that acts via membrane-bound receptors (AT-1R/AT-2R) and thereby activates hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). AT-II receptor blockers (ARBs) are thus important candidates in the treatment of liver fibrosis. Howeve... |
|
|
Bile acids induce pancreatic acinar cell injury and pancreatitis by activating calcineurin.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(1) , 570-80, (2013) Biliary pancreatitis is the leading cause of acute pancreatitis in both children and adults. A proposed mechanism is the reflux of bile into the pancreatic duct. Bile acid exposure causes pancreatic acinar cell injury through a sustained rise in cytosolic Ca(... |
|
|
Complexation of tauro- and glyco-conjugated bile salts with three neutral beta-CDs studied by ACE.
Electrophoresis 28(20) , 3745-52, (2007) Complexation of the bile salts (BS) taurocholate, tauro-beta-muricholate, taurodeoxycholate, taurochenodeoxycholate, glycocholate, glycodeoxycholate, and glycochenodeoxycholate common in rat, dog, and man with natural beta-CD and the chemically modified beta-... |
|
|
The bile acid receptor TGR5 (Gpbar-1) acts as a neurosteroid receptor in brain.
Glia 58(15) , 1794-805, (2010) TGR5 (Gpbar-1) is a membrane-bound bile acid receptor in the gastrointestinal tract and immune cells with pleiotropic actions. As shown in the present study, TGR5 is also expressed in astrocytes and neurons. Here, TGR5 may act as a neurosteroid receptor, whic... |
|
|
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces bile acid-induced apoptosis by modulation of AP-1.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 367(1) , 208-12, (2008) Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is used in the therapy of cholestatic liver diseases. Apoptosis induced by toxic bile acids plays an important role in the pathogenesis of liver injury during cholestasis and appears to be mediated by the human transcription factor... |
|
|
Ryanodine receptors contribute to bile acid-induced pathological calcium signaling and pancreatitis in mice.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 302(12) , G1423-33, (2012) Biliary pancreatitis is the most common etiology for acute pancreatitis, yet its pathophysiological mechanism remains unclear. Ca(2+) signals generated within the pancreatic acinar cell initiate the early phase of pancreatitis, and bile acids can elicit anoma... |
|
|
Taurolithocholate-induced MRP2 retrieval involves MARCKS phosphorylation by protein kinase Cϵ in HUH-NTCP Cells.
Hepatology 58(1) , 284-92, (2013) Taurolithocholate (TLC) acutely inhibits the biliary excretion of multidrug-resistant associated protein 2 (Mrp2) substrates by inducing Mrp2 retrieval from the canalicular membrane, whereas cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) increases plasma membrane (PM)... |
|
|
Longitudinal zipping/unzipping of self-assembled organic tubes.
J. Phys. Chem. B 115(49) , 14445-9, (2011) Stimuli-responsive organic tubes are an attractive supramolecular assembly which has potential applications as a controlled release vehicle. We synthesize a smart organic tube by the coassembly of lithocholic acid (LCA) and taurolithocholic acid (TLCA) in aqu... |
|
|
Identification, release and olfactory detection of bile salts in the intestinal fluid of the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis).
J. Comp. Physiol. A. Neuroethol. Sens. Neural. Behav. Physiol. 195(7) , 691-8, (2009) Olfactory sensitivity to bile salts is wide-spread in teleosts; however, which bile salts are released in sufficient quantities to be detected is unclear. The current study identified bile salts in the intestinal and bile fluids of Solea senegalensis by mass ... |