beta-(1,3)-D-Glucan
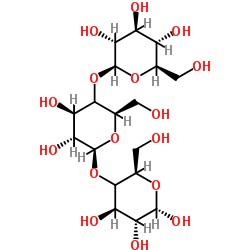
beta-(1,3)-D-Glucan structure
|
Common Name | beta-(1,3)-D-Glucan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9012-72-0 | Molecular Weight | 504.437 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 865.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H32O16 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 477.0±34.3 °C | |
|
Lipopolysaccharide and β-1,3-glucan-binding protein (LGBP) bind to seaweed polysaccharides and activate the prophenoloxidase system in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.
Dev. Comp. Immunol. 55 , 144-51, (2015) Lipopolysaccharide and β-1,3-glucan-binding protein (LGBP), important pattern recognition proteins (PRPs), recognize lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and β-1,3-glucan (βG), known as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), and subsequently trigger innate immun... |
|
|
The glucan components of the cell wall of baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) considered in relation to its ultrastructure.
Biochem. J. 114 , 557, (1969) 1. Commercial pressed baker's yeast, and cell walls prepared from it, were extracted in various ways and the products examined by a number of techniques, including infrared spectroscopy and electron microscopy. 2. The glucan components of the walls cannot be ... |
|
|
Human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 inhibits adhesion of Candida albicans by interacting with yeast cell-wall carbohydrates.
PLoS ONE 6(3) , e17755, (2011) Candida albicans is the major fungal pathogen of humans. Fungal adhesion to host cells is the first step of mucosal infiltration. Antimicrobial peptides play important roles in the initial mucosal defense against C. albicans infection. LL-37 is the only membe... |
|
|
Cell wall staining with Trypan blue enables quantitative analysis of morphological changes in yeast cells.
Front. Microbiol. 6 , 107, (2015) Yeast cells are protected by a cell wall that plays an important role in the exchange of substances with the environment. The cell wall structure is dynamic and can adapt to different physiological states or environmental conditions. For the investigation of ... |
|
|
A recombinant Sp185/333 protein from the purple sea urchin has multitasking binding activities towards certain microbes and PAMPs.
Immunobiology 221 , 889-903, (2016) The purple sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, possesses a sophisticated innate immune system that responds to microbes effectively by swift expression of the highly diverse Sp185/333 gene family. The Sp185/333 proteins are predicted to have anti-patho... |
|
|
Endogenous molecules induced by a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) elicit innate immunity in shrimp.
PLoS ONE 9 , e115232, (2014) Invertebrates rely on an innate immune system to combat invading pathogens. The system is initiated in the presence of cell wall components from microbes like lipopolysaccharide (LPS), β-1,3-glucan (βG) and peptidoglycan (PG), altogether known as pathogen-ass... |
|
|
A novel glyco-conjugate vaccine against fungal pathogens.
J. Exp. Med. 202 , 597-606, (2005) To generate a vaccine to protect against a variety of human pathogenic fungi, we conjugated laminarin (Lam), a well-characterized but poorly immunogenic beta-glucan preparation from the brown alga Laminaria digitata, with the diphtheria toxoid CRM197, a carri... |
|
|
In vitro and in silico studies on cell adhesion protein peroxinectin from Fenneropenaeus indicus and screening of heme blockers against activity.
J. Mol. Recognit. 29 , 186-98, (2016) In invertebrates, the prophenoloxidase (proPO) pathway is involved in the phenol-like antioxidant production against invading pathogens. Overproduction of melanin and phenolic substances leads to the disruption of hemocytes (own host cells); therefore, there ... |
|
|
Polyglucosan neurotoxicity caused by glycogen branching enzyme deficiency can be reversed by inhibition of glycogen synthase.
J. Neurochem. 127(1) , 101-13, (2013) Uncontrolled elongation of glycogen chains, not adequately balanced by their branching, leads to the formation of an insoluble, presumably neurotoxic, form of glycogen called polyglucosan. To test the suspected pathogenicity of polyglucosans in neurological g... |