Pyruvate carboxylase
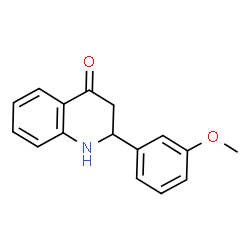
Pyruvate carboxylase structure
|
Common Name | Pyruvate carboxylase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9014-19-1 | Molecular Weight | 253.296 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 441.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H15NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 220.6±28.7 °C | |
|
Initial characterization of the human central proteome.
BMC Syst. Biol. 5 , 17, (2011) On the basis of large proteomics datasets measured from seven human cell lines we consider their intersection as an approximation of the human central proteome, which is the set of proteins ubiquitously expressed in all human cells. Composition and properties... |
|
|
The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).
Genome Res. 14 , 2121-7, (2004) The National Institutes of Health's Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) project was designed to generate and sequence a publicly accessible cDNA resource containing a complete open reading frame (ORF) for every human and mouse gene. The project initially used a r... |
|
|
Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions.
Science 325(5942) , 834-40, (2009) Lysine acetylation is a reversible posttranslational modification of proteins and plays a key role in regulating gene expression. Technological limitations have so far prevented a global analysis of lysine acetylation's cellular roles. We used high-resolution... |
|
|
The genome sequence of Propionibacterium acidipropionici provides insights into its biotechnological and industrial potential.
BMC Genomics 13 , 562, (2012) Synthetic biology allows the development of new biochemical pathways for the production of chemicals from renewable sources. One major challenge is the identification of suitable microorganisms to hold these pathways with sufficient robustness and high yield.... |
|
|
Cod liver oil ameliorates sodium nitrite-induced insulin resistance and degradation of rat hepatic glycogen through inhibition of cAMP/PKA pathway.
Life Sci. 120 , 13-21, (2015) Sodium nitrite is used to inhibit the growth of microorganisms and is responsible for the desirable red color of meat; however, it can be toxic in high quantities for humans and other animals. Moreover, glycogen, a branched polysaccharide, efficiently stores ... |
|
|
Pyruvate carboxylase as a sensitive protein biomarker for exogenous steroid chemicals.
Environ. Pollut. 189 , 184-93, (2014) Assessing protein responses to endocrine disrupting chemicals is critical for understanding the mechanisms of chemical action and for the assessment of hazards. In this study, the response of the liver proteome of male rare minnows (Gobiocypris rarus) treated... |
|
|
QM/MM study of the reaction mechanism of the carboxyl transferase domain of pyruvate carboxylase from Staphylococcus aureus.
Biochemistry 53(27) , 4455-66, (2014) Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) catalyzes the carboxylation of pyruvate to produce oxaloacetate. Its activity is directly related to insulin release and thus PC has recently attracted great interest as a potential target for diabetes treatment. In this article, the... |
|
|
Insights into the carboxyltransferase reaction of pyruvate carboxylase from the structures of bound product and intermediate analogs.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 441(2) , 377-82, (2013) Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the MgATP- and bicarbonate-dependent carboxylation of pyruvate to oxaloacetate, an important anaplerotic reaction in central metabolism. The carboxyltransferase (CT) domain of PC catalyzes ... |
|
|
A substrate-induced biotin binding pocket in the carboxyltransferase domain of pyruvate carboxylase.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(27) , 19915-25, (2013) Biotin-dependent enzymes catalyze carboxyl transfer reactions by efficiently coordinating multiple reactions between spatially distinct active sites. Pyruvate carboxylase (PC), a multifunctional biotin-dependent enzyme, catalyzes the bicarbonate- and MgATP-de... |
|
|
Functionally diverse biotin-dependent enzymes with oxaloacetate decarboxylase activity.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 544 , 75-86, (2014) Biotin-dependent enzymes catalyze carboxylation, decarboxylation and transcarboxylation reactions that participate in the primary metabolism of a wide range of organisms. In all cases, the overall reaction proceeds via two half reactions that take place in ph... |