pyrroloquinoline quinone
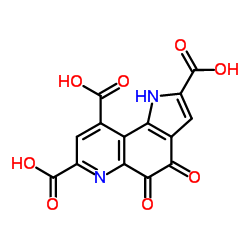
pyrroloquinoline quinone structure
|
Common Name | pyrroloquinoline quinone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 72909-34-3 | Molecular Weight | 330.206 | |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1018.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H6N2O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 569.8±34.3 °C | |
|
Molecular-level characterization of elastin-like constructs and human aortic elastin
Matrix Biol. 38 , 12-21, (2014) This study aimed to characterize the structures of two elastin-like constructs, one composed of a cross-linked elastin-like polypeptide and the other one of cross-linked tropoelastin, and native aortic elastin. The structures of the insoluble materials and hu... |
|
|
Genome-wide RNA sequencing analysis of quorum sensing-controlled regulons in the plant-associated Burkholderia glumae PG1 strain.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 7993-8007, (2015) Burkholderia glumae PG1 is a soil-associated motile plant-pathogenic bacterium possessing a cell density-dependent regulation system called quorum sensing (QS). Its genome contains three genes, here designated bgaI1 to bgaI3, encoding distinct autoinducer-1 (... |
|
|
Pyrroloquinoline-quinone suppresses liver fibrogenesis in mice.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0121939, (2015) Liver fibrosis represents the consequences of a sustained wound healing response to chronic liver injuries, and its progression toward cirrhosis is the major cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. However, anti-fibrotic treatment remains an... |
|
|
Novel Route for Agmatine Catabolism in Aspergillus niger Involves 4-Guanidinobutyrase.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 5593-603, (2015) Agmatine, a significant polyamine in bacteria and plants, mostly arises from the decarboxylation of arginine. The functional importance of agmatine in fungi is poorly understood. The metabolism of agmatine and related guanidinium group-containing compounds in... |
|
|
Pyrroloquinoline quinone modulates the kinetic parameters of the mammalian selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase 1 and is an inhibitor of glutathione reductase.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 83(6) , 815-20, (2012) Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) is a redox active cofactor for bacterial quinoproteins. Dietary PQQ also has prominent physiological effects in mammals although no mammalian quinoprotein has yet been conclusively identified. Here we found that PQQ has substant... |
|
|
Differently substituted sulfonated polyanilines: the role of polymer compositions in electron transfer with pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase.
Acta Biomater. 9(9) , 8290-8, (2013) Sulfonated polyanilines have become promising building blocks in the construction of biosensors, and therefore we use here differently substituted polymer forms to investigate the role of their structural composition and properties in achieving a direct elect... |
|
|
Coupling of pyrroloquinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase to (cytochrome c/DNA)-multilayer systems on electrodes.
Bioelectrochemistry 88 , 97-102, (2012) The redox protein cytochrome c (cyt c) assembles into electro-active multilayers on gold electrodes by the help of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as a negatively-charged building block. The feasibility of this electro-active system as a novel interface for the i... |
|
|
Pyrroloquinoline quinone against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in cultured neural stem and progenitor cells.
Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 42 , 37-45, (2015) Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), as a well-known redox enzyme cofactor, has been proven to play important roles in the regulation of cellular growth and development in mammals. Numerous physiological and medicinal functions of PQQ have so far been reported alt... |
|
|
High-temperature sorbose fermentation with thermotolerant Gluconobacter frateurii CHM43 and its mutant strain adapted to higher temperature.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 95(6) , 1531-40, (2012) We succeeded in obtaining a strain adapted to higher temperature from a thermotolerant strain, Gluconobacter frateurii CHM43, for sorbose fermentation. The adapted strain showed higher growth and L-sorbose production than original CHM43 strain at higher tempe... |
|
|
Pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthesis gene pqqC, a novel molecular marker for studying the phylogeny and diversity of phosphate-solubilizing pseudomonads.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77(20) , 7345-54, (2011) Many root-colonizing pseudomonads are able to promote plant growth by increasing phosphate availability in soil through solubilization of poorly soluble rock phosphates. The major mechanism of phosphate solubilization by pseudomonads is the secretion of gluco... |