Brinzolamide
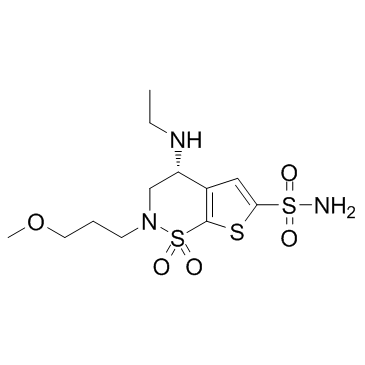
Brinzolamide structure
|
Common Name | Brinzolamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 138890-62-7 | Molecular Weight | 383.507 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 586.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H21N3O5S3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 308.2±32.9 °C | |
|
Optimization of methazolamide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for ophthalmic delivery using Box-Behnken design.
J. Liposome Res. 24(3) , 171-81, (2014) The purpose of the present study was to optimize methazolamide (MTZ)-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) which were used as topical eye drops by evaluating the relationship between design factors and experimental data. A three factor, three-level Box-Behn... |
|
|
Soluble CD44 and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with acute primary angle closure.
Acta Ophthalmol. 93 , e261-5, (2015) Acute elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP) in acute primary angle closure (APAC) can cause huge damage to the variable cells in the eye; however, the mechanisms that connect the two processes still remain unclear. In this study, we aim to evaluate the leve... |
|
|
Meta-analysis of α2-adrenergic agonists versus carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as adjunctive therapy.
Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 28(4) , 543-50, (2012) To evaluate the efficacy of α2-adrenergic agonist (AA) brimonidine and topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) dorzolamide and brinzolamide in reducing intraocular pressure (IOP) when used as adjunctive therapy to β-blockers (BBs) or prostaglandin analog... |
|
|
Brinzolamide 1%/timolol 0.5%: safety and efficacy of a new fixed-combination IOP-lowering product for glaucoma.
Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 26(11) , 2575-8, (2010) To provide a commentary on recent studies with the new IOP-lowering fixed-combination product brinzolamide 1%/timolol 0.5%.Medline was searched for brinzolamide/timolol fixed-combination clinical literature (up to May 18, 2010) and the current comprehensive b... |
|
|
Timolol versus brinzolamide added to travoprost in glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 249(7) , 1065-71, (2011) To compare the efficacy and safety of timolol 0.5% versus brinzolamide 1.0% when added to travoprost monotherapy in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.Patients meeting selection criteria (IOP one eye 19 mmHg and ≤32 mmHg and IOP ... |
|
|
Effect of Dorzolamide/Timolol or Brinzolamide/Timolol prophylaxis on intravitreal anti-VEGF injection-induced intraocular hypertension.
Semin. Ophthalmol. 28(2) , 61-7, (2013) To evaluate prospectively whether anti-glaucomatic drugs administered prior to intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injection bevacizumab (Avastin,® Roche) or ranibizumab (Lucentis,® Novartis) prevents intraocular hypertension after the... |
|
|
Brinzolamide.
Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 9(4) , 653-62, (2008) Primary open-angle glaucoma is a multifactorial optic neuropathy characterized by the progressive loss of retinal ganglion cells and their axons. However, the primary risk factor is elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), which can damage the optic nerve head (O... |
|
|
Efficacy of single glaucoma drug in combined timolol XE, latanoprost and brinzolamide therapy: a discontinuation study.
J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 28(3) , 245-50, (2012) To study the efficacy of a single drug in patients with primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension who were receiving timolol XE 0.5%, latanoprost 0.005% and brinzolamide 1% with its discontinuation.Sixty patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular h... |
|
|
[Mode of action, clinical profile and relevance of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in glaucoma therapy].
Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 230(2) , 146-9, (2013) Since their introduction the local carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAH) dorzolamide and brinzolamide have become well established in the drug therapy of glaucoma. They lower intraocular pressure (IOP) by blocking specifically carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary ... |
|
|
Brinzolamide/brimonidine (Simbrinza) for glaucoma.
Med. Lett. Drugs Ther. 55(1421) , 57-8, (2013)
|