Margatoxin
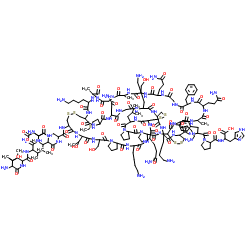
Margatoxin structure
|
Common Name | Margatoxin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 145808-47-5 | Molecular Weight | N/A | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C178H286N52O50S7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Evidence for aconitine-induced inhibition of delayed rectifier K(+) current in Jurkat T-lymphocytes.
Toxicology 289(1) , 11-8, (2011) Aconitine (ACO) is a highly toxic diterpenoid alkaloid and known to exert the immunomodulatory action. However, whether it has any effects on ion currents in immune cells remains unknown. The effects of ACO and other related compounds on ion currents in Jurka... |
|
|
Charybdotoxin and margatoxin acting on the human voltage-gated potassium channel hKv1.3 and its H399N mutant: an experimental and computational comparison.
J. Phys. Chem. B 116(17) , 5132-40, (2012) The effect of the pore-blocking peptides charybdotoxin and margatoxin, both scorpion toxins, on currents through human voltage-gated hK(v)1.3 wild-type and hK(v)1.3_H399N mutant potassium channels was characterized by the whole-cell patch clamp technique. In ... |
|
|
Contribution of Kv2.1 channels to the delayed rectifier current in freshly dispersed smooth muscle cells from rabbit urethra.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 301(5) , C1186-200, (2011) We have characterized the native voltage-dependent K(+) (K(v)) current in rabbit urethral smooth muscle cells (RUSMC) and compared its pharmacological and biophysical properties with K(v)2.1 and K(v)2.2 channels cloned from the rabbit urethra and stably expre... |
|
|
Potassium secretion by voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 in the rat kidney.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 299(1) , F255-64, (2010) The fine regulation of Na(+) and K(+) transport takes place in the cortical distal nephron. It is well established that K(+) secretion occurs through apical K(+) channels: the ROMK and the Ca(2+)- and voltage-dependent maxi-K. Previously, we identified the vo... |
|
|
Involvement of Kv1.3 and p38 MAPK signaling in HIV-1 glycoprotein 120-induced microglia neurotoxicity.
Cell Death Dis. 3 , e254, (2012) Inflammatory responses mediated by activated microglia play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-associated neurocognitive disorders. Studies on identification of specific targets to control microglia activation an... |
|
|
Pharmacological inhibition of Kv1.3 fails to modulate insulin sensitivity in diabetic mice or human insulin-sensitive tissues.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 301(2) , E380-90, (2011) Genetic ablation of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 improves insulin sensitivity and increases metabolic rate in mice. Inhibition of Kv1.3 in mouse adipose and skeletal muscle is reported to increase glucose uptake through increased GLUT4 translocat... |
|
|
Kv1.3 channels regulate synaptic transmission in the nucleus of solitary tract.
J. Neurophysiol. 105(6) , 2772-80, (2011) The voltage-gated K(+) channel Kv1.3 has been reported to regulate transmitter release in select central and peripheral neurons. In this study, we evaluated its role at the synapse between visceral sensory afferents and secondary neurons in the nucleus of the... |
|
|
Lymphocyte activation in type 1 diabetes mellitus: the increased significance of Kv1.3 potassium channels.
Immunol. Lett. 133(1) , 35-41, (2010) Kv1.3 and IKCa1 potassium channels participate in the maintenance of calcium-influx during lymphocyte activation. Kv1.3 channels have a prominent role in specific T cell subsets, presenting a possible target for selective immunomodulation. We investigated the... |
|
|
T-lymphocyte calcium influx characteristics and their modulation by Kv1.3 and IKCa1 channel inhibitors in the neonate.
Int. Immunol. 22(9) , 769-74, (2010) Cytokine production in activated T lymphocytes of the term neonate is reduced compared with adults. We aimed to characterize the calcium influx kinetics of activated T lymphocytes in the neonate and to test the functionality and expression of Kv1.3 and IKCa1 ... |
|
|
Different potassium channels are involved in relaxation of rat renal artery induced by P1075.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 111(1) , 24-30, (2012) The ATP-sensitive K(+) channels opener (K(ATP)CO), P1075 [N-cyano-N'-(1,1-dimethylpropyl)-N″-3-pyridylguanidine], has been shown to cause relaxation of various isolated animal and human blood vessels by opening of vascular smooth muscle ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(... |