Phospholipase D
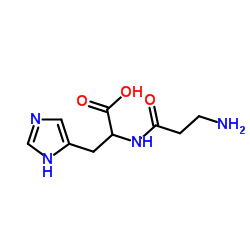
Phospholipase D structure
|
Common Name | Phospholipase D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9001-87-0 | Molecular Weight | 226.232 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 656.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H14N4O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 350.7±31.5 °C | |
|
Initial characterization of the human central proteome.
BMC Syst. Biol. 5 , 17, (2011) On the basis of large proteomics datasets measured from seven human cell lines we consider their intersection as an approximation of the human central proteome, which is the set of proteins ubiquitously expressed in all human cells. Composition and properties... |
|
|
Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks.
Cell 127(3) , 635-648, (2006) Cell signaling mechanisms often transmit information via posttranslational protein modifications, most importantly reversible protein phosphorylation. Here we develop and apply a general mass spectrometric technology for identification and quantitation of pho... |
|
|
A quantitative atlas of mitotic phosphorylation.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105(31) , 10762-7, (2008) The eukaryotic cell division cycle is characterized by a sequence of orderly and highly regulated events resulting in the duplication and separation of all cellular material into two newly formed daughter cells. Protein phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kin... |
|
|
The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).
Genome Res. 14 , 2121-7, (2004) The National Institutes of Health's Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) project was designed to generate and sequence a publicly accessible cDNA resource containing a complete open reading frame (ORF) for every human and mouse gene. The project initially used a r... |
|
|
The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment.
Genome Res. 13(10) , 2265-70, (2003) A large-scale effort, termed the Secreted Protein Discovery Initiative (SPDI), was undertaken to identify novel secreted and transmembrane proteins. In the first of several approaches, a biological signal sequence trap in yeast cells was utilized to identify ... |
|
|
Glycoproteomics analysis of human liver tissue by combination of multiple enzyme digestion and hydrazide chemistry.
J. Proteome Res. 8(2) , 651-61, (2009) The study of protein glycosylation has lagged far behind the progress of current proteomics because of the enormous complexity, wide dynamic range distribution and low stoichiometric modification of glycoprotein. Solid phase extraction of tryptic N-glycopepti... |
|
|
Arabidopsis acyl-CoA-binding protein ACBP1 participates in the regulation of seed germination and seedling development.
Plant J. 74(2) , 294-309, (2013) A family of six genes encoding acyl-CoA-binding proteins (ACBPs), ACBP1-ACBP6, has been characterized in Arabidopsis thaliana. In this study, we demonstrate that ACBP1 promotes abscisic acid (ABA) signaling during germination and seedling development. ACBP1 w... |
|
|
Francisella tularensis LVS induction of prostaglandin biosynthesis by infected macrophages requires specific host phospholipases and lipid phosphatases.
Infect. Immun. 82(8) , 3299-311, (2014) Francisella tularensis induces the synthesis of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) by infected macrophages to alter host immune responses, thus providing a survival advantage to the bacterium. We previously demonstrated that PGE(2) synthesis by F. tularensis-infecte... |
|
|
Molecular mechanisms of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced superoxide generation and degranulation in mouse neutrophils: phospholipase D is dispensable.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 33(1) , 136-45, (2013) Phospholipase D (PLD), which produces the lipid messenger phosphatidic acid (PA), has been implicated in superoxide generation and degranulation in neutrophils. The basis for this conclusion is the observation that primary alcohols, which interfere with PLD-c... |
|
|
Phospholipase D activates HIF-1-VEGF pathway via phosphatidic acid.
Exp. Mol. Med. 46 , e126, (2014) Growth factor-stimulated phospholipase D (PLD) catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine (PC), generating phosphatidic acid (PA) which may act as a second messenger during cell proliferation and survival. Therefore, PLD is believed to play an important ... |