FLB 131
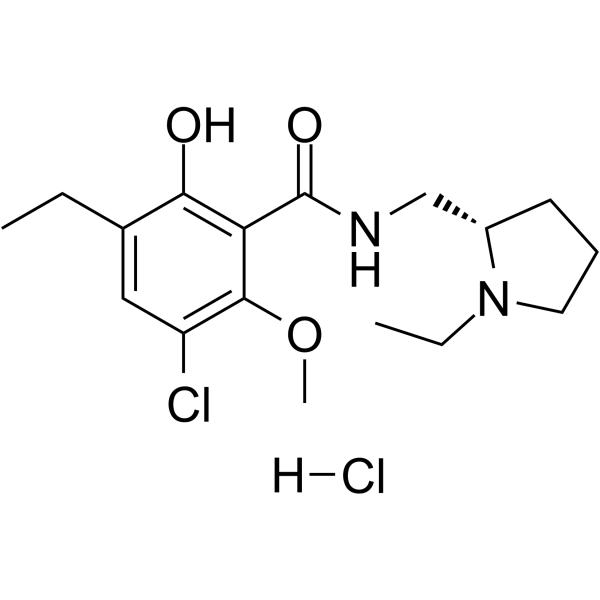
FLB 131 structure
|
Common Name | FLB 131 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 97612-24-3 | Molecular Weight | 377.306 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H26Cl2N2O3 | Melting Point | 144 - 146 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Dopamine D2 receptor activity modulates Akt signaling and alters GABAergic neuron development and motor behavior in zebrafish larvae.
J. Neurosci. 31 , 5512-25, (2011) An imbalance in dopamine-mediated neurotransmission is a hallmark physiological feature of neuropsychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia. Recent evidence demonstrates that dopamine D(2) receptors, which are the main target of antipsychotics, modulate the ... |
|
|
Dopamine D2 receptors are involved in the regulation of Fyn and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 phosphorylation in the rat striatum in vivo.
J. Neurosci. Res. 94 , 329-38, (2016) Fyn, a major Src family kinase (SFK) member that is densely expressed in striatal neurons, is actively involved in the regulation of cellular and synaptic activities in local neurons. This SFK member is likely regulated by dopamine signaling through a recepto... |
|
|
Some in vitro receptor binding properties of [3H]eticlopride, a novel substituted benzamide, selective for dopamine-D2 receptors in the rat brain.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 111 , 191-199, (1985) The substituted benzamide compound eticlopride, (S)-(-)-5-chloro-3-ethyl-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) methyl]-6-methoxysalicylamide hydrochloride (FLB 131), has been shown to selectively block dopamine-D2 binding sites in the rat brain. The compound was tritiu... |
|
|
Regional in vivo binding of the substituted benzamide [3H]eticlopride in the rat brain: evidence for selective labelling of dopamine receptors.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 120 , 217-226, (1986) The novel substituted benzamide eticlopride, (S)-(-)-5-chloro-3-ethyl-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-6-methoxy salicylamide hydrochloride (A38503; FLB 131), was radiolabelled to high specific activity and used for in vivo receptor binding studies in the r... |
|
|
Dopamine regulates angiogenesis in normal dermal wound tissues.
PLoS ONE 6(9) , e25215, (2011) Cutaneous wound healing is a normal physiological process and comprises different phases. Among these phases, angiogenesis or new blood vessel formation in wound tissue plays an important role. Skin is richly supplied by sympathetic nerves and evidences indic... |