POLY(BIS(2 2 2-TRIFLUOROETHOXY)PHOSPHAZ&
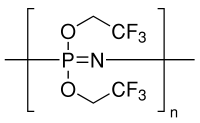
POLY(BIS(2 2 2-TRIFLUOROETHOXY)PHOSPHAZ& structure
|
Common Name | POLY(BIS(2 2 2-TRIFLUOROETHOXY)PHOSPHAZ& | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 28212-50-2 | Molecular Weight | N/A | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | (C4H4F6NPO2)n | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Properties and clinical development of a novel coating technology: the poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene].
Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 4(1) , 18-22, (2010) Ultrapure poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene] is a novel biocompatible, anti-inflammatory, antithrombogenic polymer which has the potential to cover stent devices without elution of a cell cycle inhibiting drug. The properties of polyphosphazene are likely ... |
|
|
A new polymer concept for coating of vascular stents using PTFEP (poly(bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene) to reduce thrombogenicity and late in-stent stenosis.
Invest. Radiol. 40(4) , 210-8, (2005) We sought to evaluate the new polymer PTFEP (poly(bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene) for (1) its ability to reduce thrombogenicity and late in-stent stenosis and (2) its effect on endothelialization in a rabbit iliac artery model.Nanocoated ( approximately 50 n... |
|
|
The efficacy of nanoscale poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy) phosphazene] (PTFEP) coatings in reducing thrombogenicity and late in-stent stenosis in a porcine coronary artery model.
Invest. Radiol. 42(5) , 303-11, (2007) Previous experimental studies have demonstrated that poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene] (PTFEP) nanocoated stents have antithrombotic characteristics, reduce in-stent stenosis, prevent wall inflammation, and do not hamper endothelialization. This study was... |
|
|
Radiation grafting of hydrophilic monomers onto poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene].
Biomaterials 15(11) , 937-43, (1994) The hydrophilic monomers dimethylacrylamide (DMAA) and acrylamide (AAm) were radiation grafted onto poly[bis-(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene] (PTFP) for biocompatibility enhancement through direct irradiation of the polymer films immersed in monomer-solvent mixt... |
|
|
Polyphosphazenes as biomaterials: surface modification of poly(bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene) with polyethylene glycols.
Biomaterials 14(6) , 430-6, (1993) Investigations were carried out on the metathetical exchange reaction between the -O-CH2CF3 moieties of poly(bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene) (PTFP), in the state of slightly swollen films, and the alkoxide ions derived from methoxypolyethylene glycol (MPEG) ... |
|
|
Arterial distribution characteristics of Embozene particles and comparison with other spherical embolic agents in the porcine acute embolization model.
J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 20(12) , 1597-607, (2009) To determine the arterial distribution pattern of the embolic agent Embozene within the porcine kidney and compare it with those of other spherical embolic agents.Embozene, Embosphere, Bead Block, and Contour SE in size classes of 100-300 microm, 500-700 micr... |
|
|
Long-term biocompatibility evaluation of a novel polymer-coated stent in a porcine coronary stent model.
Coron. Artery Dis. 14(5) , 401-8, (2003) Polymer coatings have been used to modify the surface of stents and to serve as a matrix for local drug delivery.Bare stainless steel stents or poly-bis-trifluorethoxy phosphazene (PTFEP) dip-coated stents (Coroflex, Germany) were randomly implanted into porc... |
|
|
Chemotactic penetration of keratocytes in ePTFE polymer in vitro.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 56(4) , 487-93, (2001) Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is used as a support for artificial corneas. Implanted in corneas, most of the time this polymer is colonized by corneal host cells. The absence of colonization often coincides with extrusion of the polymer. Therefore,... |
|
|
Efficacy of a polyphosphazene nanocoat in reducing thrombogenicity, in-stent stenosis, and inflammatory response in porcine renal and iliac artery stents.
J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 19(3) , 427-37, (2008) It is hypothesized that the inorganic polymer poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene] (PTFEP) reduces stent-associated thrombosis, in-stent stenosis, and inflammatory response and stimulates reendothelialization in a porcine model.PTFEP-nanocoated and bare stai... |
|
|
Improved osseointegration of PTFEP-coated titanium implants.
Med. Sci. Monit. 14(2) , BR35-40, (2008) Clinical success of bone implants is critically related to the interaction between the implant surface and the surrounding tissue. The polymer poly(bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene) (PTFEP) is a promising, highly biocompatible surface coating which also inhibi... |