Starch soluble
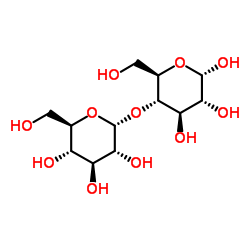
Starch soluble structure
|
Common Name | Starch soluble | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9005-84-9 | Molecular Weight | 342.297 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 667.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H22O11 | Melting Point | 256-258 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 357.8±31.5 °C | |
|
Allomorph distribution and granule structure of lotus rhizome C-type starch during gelatinization.
Food Chem. 142 , 408-15, (2014) The allomorph distribution and granule structure of C-type starch from lotus rhizomes were investigated using a combination of techniques during gelatinization. The disruption of crystallinity during gelatinization began from the end distant from the eccentri... |
|
|
Solar energy assisted starch-stabilized palladium nanoparticles and their application in C-C coupling reactions.
J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13(7) , 5061-8, (2013) Present work reports a novel one step, greener protocol for the synthesis of starch-stabilized palladium nanoparticles (PdNPs) with an average particle diameter of 30-40 nm. These particles were stable and uniform in size. In present protocol, the concentrate... |
|
|
Starch/polyvinyl alcohol blended materials used as solid carbon source for tertiary denitrification of secondary effluent.
J. Environ. Sci. (China) 25(10) , 1972-9, (2013) Starch/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) blended materials for using as a solid carbon source (SCS) were prepared by blending PVA and gelatinized starch in an aqueous solution system, in which PVA served as framework material and starch as carbon source. The optimizati... |
|
|
Synthesis of thermal and chemical resistant oxygen barrier starch with reinforcement of nano silicon carbide.
Carbohydr. Polym. 97(2) , 758-63, (2013) Starch/silicon carbide (starch/SiC) bionanocomposites were synthesized by solution method using different wt% of silicon carbide with starch matrix. The interaction between starch and silicon carbide was studied by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrosco... |
|
|
Effect of harvesting periods on the chemical and pasting properties of trifoliate yam flour.
Food Chem. 142 , 159-65, (2014) The effects of delayed harvesting on the chemical and pasting properties of trifoliate yam flour were studied. The tubers were harvested at 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11months after maturity and were processed into flours. Chemical and pasting properties of the flours w... |
|
|
Enzymatic conversions of starch.
Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 68 , 59-436, (2012) This article surveys methods for the enzymatic conversion of starch, involving hydrolases and nonhydrolyzing enzymes, as well as the role of microorganisms producing such enzymes. The sources of the most common enzymes are listed. These starch conversions are... |
|
|
Novel role of ZmaNAC36 in co-expression of starch synthetic genes in maize endosperm.
Plant Mol. Biol. 84(3) , 359-69, (2014) Starch is an essential commodity that is widely used as food, feed, fuel and in industry. However, its mechanism of synthesis is not fully understood, especially in terms of the expression and regulation of the starch synthetic genes. It was reported that the... |
|
|
Enzymatic acylation of starch
Bioresour. Technol. 115 , 41-7, (2012) Highlights ► Several reports of enzyme-catalysed attachment of longer acyl chains to starch. ► Hard to achieve necessary contact between starch, acyl donor and enzyme. ► Varied aqueous and organic media, and approaches to solubilise some components. ► Require... |
|
|
Improving starch yield in cereals by over-expression of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase: expectations and unanticipated outcomes.
Plant Sci. 211 , 52-60, (2013) Significant improvements in crop productivity are required to meet the nutritional requirements of a growing world population. This challenge is magnified by an increased demand for bioenergy as a means to mitigate carbon inputs into the environment. Starch i... |
|
|
Morphology and structural properties of high-amylose rice starch residues hydrolysed by amyloglucosidase.
Food Chem. 138(4) , 2089-98, (2013) High-amylose starches are attracting considerable attention because of their potential health benefits and industrial uses. Enzyme hydrolysis of starch is involved in many biological and industrial processes. In this paper, starches were isolated from high-am... |