4-Phytase
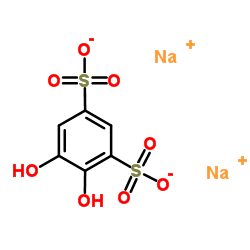
4-Phytase structure
|
Common Name | 4-Phytase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9001-89-2 | Molecular Weight | 314.201 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Na2O8S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Polyphosphates and pyrophosphates of hexopyranoses as allosteric effectors of human hemoglobin: synthesis, molecular recognition, and effect on oxygen release.
ChemMedChem 6(1) , 153-68, (2011) Polyphosphorylated and perphosphorylated hexopyranose monosaccharides and disaccharides were synthesized from parent or partially protected carbohydrates as potential allosteric effectors of hemoglobin. A study toward the construction of seven- and eight-memb... |
|
|
A type IV translocated Legionella cysteine phytase counteracts intracellular growth restriction by phytate.
J. Biol. Chem. 289(49) , 34175-88, (2014) The causative agent of Legionnaires' pneumonia, Legionella pneumophila, colonizes diverse environmental niches, including biofilms, plant material, and protozoa. In these habitats, myo-inositol hexakisphosphate (phytate) is prevalent and used as a phosphate s... |
|
|
Genetic diversity and expression profiles of cysteine phytases in the sheep rumen during a feeding cycle.
Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 59(6) , 615-20, (2014) Cysteine phytase is the main phytate-degrading enzyme of ruminant animals. To explore the genetic diversity and dynamic expression profile of cysteine phytase in sheep rumen during a feeding cycle, four transcript (0, 4, 9 and 16 h after feeding) and one DNA ... |
|
|
Extra-phosphoric effects of phytase with and without xylanase in corn-soybean meal-based diets fed to broilers.
Poult. Sci. 92(4) , 979-91, (2013) Two experiments were conducted to evaluate the extra-phosphoric effects of phytase on amino acid (AA) and energy digestibility (experiments 1 and 2) and growth performance (experiment 2) of broilers fed diets adequate in Ca and nonphytate P supplemented with ... |
|
|
Marker type but not concentration influenced apparent ileal amino acid digestibility in phytase-supplemented diets for broiler chickens and pigs.
J. Anim. Sci. 90(12) , 4414-20, (2012) Two experiments were conducted to investigate whether the choice of digestibility marker or marker concentration in corn-soybean meal diets influence apparent ileal AA digestibility (AIAAD) or the potential phytase-induced improvement in AIAAD in broiler chic... |
|
|
Influence of superdoses of a novel microbial phytase on growth performance, tibia ash, and gizzard phytate and inositol in young broilers.
Poult. Sci. 93(5) , 1172-7, (2014) An experiment was conducted to evaluate the influence of a novel microbial phytase on performance, tibia ash, and the content of phytate, phytate esters, and inositol in the gizzard of young broilers. Male Cobb 500 broilers (n = 1,680) were fed 1 of 7 experim... |
|
|
Phytase transgenic corn in nutrition of laying hens: residual phytase activity and phytate phosphorus content in the gastrointestinal tract.
Poult. Sci. 92(11) , 2923-9, (2013) The residual activities of transgenic corn-derived and 2 commercial microbial phytases (PA and PB) along the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of laying hens were compared to evaluate their relative resistance to hydrolysis in the GIT when added to P-deficient die... |
|
|
PCR-RFLP analysis of the diversity of phytate-degrading bacteria in the Tibetan Plateau.
Can. J. Microbiol. 59(4) , 245-51, (2013) Phytases play a very important role in increasing phytate digestion and reducing phosphorus pollution in the environment, and phytate-degrading bacteria have a ubiquitous distribution in the environment. Due to its extremely harsh environment, the Tibetan Pla... |
|
|
Effect of calcium level and phytase addition on ileal phytate degradation and amino acid digestibility of broilers fed corn-based diets.
Poult. Sci. 93(4) , 906-15, (2014) This study investigated the effect of dietary Ca to available P (AvP) ratio and phytase supplementation on bone ash, ileal phytate degradation, and nutrient digestibility in broilers fed corn-based diets. The experimental design was a 4 × 2 factorial arrangem... |
|
|
Phytic acid degrading lactic acid bacteria in tef-injera fermentation.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 190 , 54-60, (2014) Ethiopian injera, a soft pancake, baked from fermented batter, is preferentially prepared from tef (Eragrostis tef) flour. The phytic acid (PA) content of tef is high and is only partly degraded during the fermentation step. PA chelates with iron and zinc in ... |