Locust bean gum
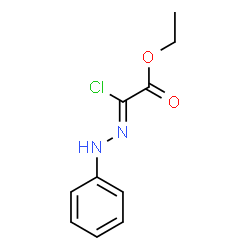
Locust bean gum structure
|
Common Name | Locust bean gum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9000-40-2 | Molecular Weight | 226.65954 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 308.7±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H11ClN2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 140.5±23.2 °C | |
|
Determination of D-pinitol in carob syrup.
Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 62(6) , 572-6, (2011) Carob syrup is a traditional product native to the Mediterranean region, containing a high concentration of sugar, phenolic compounds and minerals. d-pinitol is a bioactive component extracted from legumes and has some beneficial effects on human metabolism. ... |
|
|
Purification and characterization of Aspergillus terreus α-galactosidases and their use for hydrolysis of soymilk oligosaccharides.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 164(7) , 1111-25, (2011) α-Galactosidases has the potential to hydrolyze α-1-6 linkages in raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFO). Aspergillus terreus cells cultivated on wheat bran produced three extracellular forms of α-galactosidases (E1, E2, and E3). E1 and E2 α-galactosidases p... |
|
|
Efficacy of the combined application of chitosan and Locust Bean Gum with different citrus essential oils to control postharvest spoilage caused by Aspergillus flavus in dates.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 170 , 21-8, (2014) This study reports the efficacy of the combined application of chitosan (CH) and Locust Bean Gum (LBG) in combination with different citrus essential oils (EOs) to inhibit Aspergillus flavus in vitro and on artificially infected dates for a storage period of ... |
|
|
Expression of Trichoderma reesei β-mannanase in tobacco chloroplasts and its utilization in lignocellulosic woody biomass hydrolysis.
PLoS ONE 6(12) , e29302, (2011) Lignocellulosic ethanol offers a promising alternative to conventional fossil fuels. One among the major limitations in the lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis is unavailability of efficient and environmentally biomass degrading technologies. Plant-based produ... |
|
|
Influence of a family 29 carbohydrate binding module on the activity of galactose oxidase from Fusarium graminearum.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1860 , 354-62, (2015) Galactose oxidase (GaO) selectively oxidizes the primary hydroxyl of galactose to a carbonyl, facilitating targeted chemical derivatization of galactose-containing polysaccharides, leading to renewable polymers with tailored physical and chemical properties. ... |
|
|
A new approach for the synthesis of hyperbranched N-glycan core structures from locust bean gum.
Org. Lett. 15(24) , 6278-81, (2013) A novel protocol for the synthesis of general N-glycan core structures was established by means of Manβ(1→4)Man peracetate derived from a naturally abundant locust bean gum as a key starting material. Phenyl (2-O-benzyl-4,6-O-benzylidine-β-D-mannopyranosyl)-(... |
|
|
Locust bean gum as superdisintegrant--formulation and evaluation of nimesulide orodispersible tablets.
Polim. Med. 41(1) , 17-28, (2011) Orodispersible tablets disperse instantaneously in the mouth so that they can be swallowed without the aid of water. The aim of the present study was to formulate nimesulide orodispersible tablets using locust bean gum as a natural superdisintegrant. The gum ... |
|
|
Food gels: gelling process and new applications.
Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr 52(4) , 334-46, (2012) Food gels are viscoelastic substances and several gelled products are manufactured throughout the world. The gelling agents in foods are usually polysaccharides and proteins. In food gels, the polymer molecules are not cross-linked by covalent bonds with the ... |
|
|
Phytochemical profile, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of the carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua L.) germ flour extracts.
Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 66(1) , 78-84, (2011) This work aimed to evaluate the phytochemical content and to determine the antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of methanol extracts of the carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua L.) germ flour. The extracts were rich in phenolic compounds, had considerable antioxidan... |
|
|
Process design and economic analysis of a hypothetical bioethanol production plant using carob pod as feedstock.
Bioresour. Technol. 104 , 324-8, (2012) A process for the production of ethanol from carob (Ceratonia siliqua) pods was designed and an economic analysis was carried out for a hypothetical plant. The plant was assumed to perform an aqueous extraction of sugars from the pods followed by fermentation... |