3-Hydroxy-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
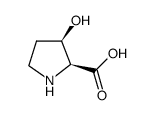
3-Hydroxy-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-Hydroxy-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4298-05-9 | Molecular Weight | 131.13000 | |
| Density | 1.395g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 355.233ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO3 | Melting Point | 232ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 168.639ºC | |
|
Novel proline hydroxylase activities in the pneumocandin-producing fungus Glarea lozoyensis responsible for the formation of trans 3- and trans 4-hydroxyproline.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62(2-3) , 263-7, (2003) Novel proline 3-hydroxylase (P3H) and proline 4-hydroxylase (P4H) activities that convert free l-proline to both trans 3- and trans 4-hydroxy- l-proline were detected in protein extracts of the anamorphic fungus Glarea lozoyensis. The enzymatic conversion of ... |
|
|
Insights on the evolution of prolyl 3-hydroxylation sites from comparative analysis of chicken and Xenopus fibrillar collagens.
PLoS ONE 6(5) , e19336, (2011) Recessive mutations that prevent 3-hydroxyproline formation in type I collagen have been shown to cause forms of osteogenesis imperfecta. In mammals, all A-clade collagen chains with a GPP sequence at the A1 site (P986), except α1(III), have 3Hyp at residue P... |
|
|
Conformational studies of peptides containing cis-3-hydroxy-D-proline.
J. Org. Chem. 69(21) , 7399-402, (2004) Conformational analysis of peptides containing cis-3-hydroxy-d-proline (d-cis-3-Hyp) by NMR studies revealed that the 3-hydroxyl group in this amino acid plays a significant role in the overall three-dimensional structures of the peptides. When the d-cis-3-Hy... |
|
|
Pneumocandins from Zalerion arboricola. V. Glutamic acid- and leucine-derived amino acids in pneumocandin A0 (L-671,329) and distinct origins of the substituted proline residues in pneumocandins A0 and B0.
J. Antibiot. 45(12) , 1953-7, (1992)
|
|
|
Identification of 3-hydroxyproline residues in several proteins of Fasciola hepatica.
Exp. Parasitol. 82(1) , 69-72, (1996)
|
|
|
Separation and evaluation of the cis and trans isomers of hydroxyprolines: effect of hydrolysis on the epimerization.
Anal. Biochem. 137(1) , 151-5, (1984) A procedure has been developed which can detect the hydroxyproline isomers trans-4-hydroxyproline (Hyp), trans-3-hydroxyproline, cis-4-hydroxyproline, and cis-3-hydroxyproline present in hydrolysates of collagens. The method involves hydrolyzing collagen, and... |
|
|
Simplified procedure for the analysis of 3- and 4-hydroxyproline.
J. Chromatogr. A. 227(2) , 341-8, (1982) A column chromatographic analysis for 3-hydroxyproline (3-Hyp), 4-hydroxyproline (4-Hyp), and gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) is described. The analyses of urine and plasma were performed with a JLC-6AH amino acid analyzer. A 0.15 M sodium citrate buffer, pH... |
|
|
Bovine renal cortex type I collagen: high contents of 3- and 4-hydroxyprolines.
J. Biochem. 89(5) , 1397-401, (1981) Type I collagen was prepared from bovine renal cortices by pepsin digestion followed by differential salt fractionation, and was identified by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, CM-cellulose chromatography, and by the analysis of CNBr-cleavage products o... |
|
|
A new rapid method for quantitating radioactive proline, 4-hydroxyproline, and 3-hydroxyproline.
Anal. Biochem. 102(2) , 291-9, (1980)
|
|
|
Increased renal excretion of 3 hydroxyproline in patients with active glomerular nephropathies and with polycystic renal disease.
Clin. Nephrol. 17(2) , 64-9, (1982) The renal excretion of 3 hydroxyproline (3 HYP) and 4 hydroxyproline (4 HYP) was investigated in control subjects and in patients with various renal diseases. In normal adult subjects urinary 3 HYP was 12.5 +/- 3.5 (SD) mumoles/24 hr, 4 HYP was 226 +/- 62 mum... |