Maltopentaose
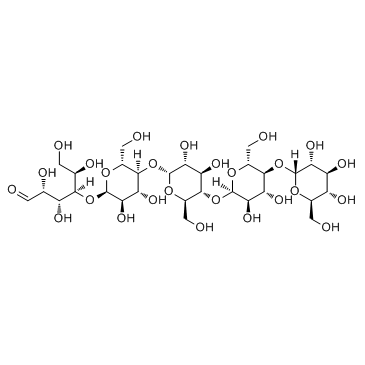
Maltopentaose structure
|
Common Name | Maltopentaose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34620-76-3 | Molecular Weight | 788.654 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1248.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H52O26 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 709.1±34.3 °C | |
|
Microbiota and metabolites of aged bottled gueuze beers converge to the same composition.
Food Microbiol. 47 , 1-11, (2015) Gueuze beers are prepared by mixing young and old lambic beers and are bottle-refermented spontaneously for aging. The present study analyzed the microbiota and metabolites present in gueuze beers that were aged between a few months and up to 17 years. Yeasts... |
|
|
Octanoylation of early intermediates of mycobacterial methylglucose lipopolysaccharides.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13610, (2015) Mycobacteria synthesize unique intracellular methylglucose lipopolysaccharides (MGLP) proposed to modulate fatty acid metabolism. In addition to the partial esterification of glucose or methylglucose units with short-chain fatty acids, octanoate was invariabl... |
|
|
UP-HILIC-MS/MS to Determine the Action Pattern of Penicillium sp. Dextranase.
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 26 , 1174-85, (2015) Investigation of the action pattern of enzymes acting on carbohydrates is challenging, as both the substrate and the digestion products are complex mixtures. Dextran and its enzyme-derived oligosaccharides are widely used for many industrial applications. In ... |
|
|
Interaction of bacteriophage lambda with its cell surface receptor: an in vitro study of binding of the viral tail protein gpJ to LamB (Maltoporin).
Biochemistry 45(8) , 2708-20, (2006) The cell surface receptor for bacteriophage Lambda is LamB (maltoporin). Responsible for phage binding to LamB is the C-terminal part, gpJ, of phage tail protein J. To study the interaction between LamB and gpJ, a chimera protein composed of maltose binding p... |
|
|
Competitive and product inhibition-based alpha-amylase activity analysis method.
Clin. Biochem. 41(4-5) , 325-30, (2008) To propose a methodology for analyzing salivary alpha-amylase activity (sAMY) for a hand-held device that can be used easily and quickly for evaluating human psychological effects.An improved method for the analysis of sAMY is proposed using competitive and p... |
|
|
Expression and purification of cellulase Xf818 from Xylella fastidiosa in Escherichia coli.
Curr. Microbiol. 53(3) , 198-203, (2006) Xylella fastidiosa was the first plant pathogen whose complete genome sequence was available. X. fastidiosa causes citrus variegated chlorosis, but the physiological basis of the disease in unknown. Through comparative sequence analysis, several putative plan... |
|
|
Cellulase production from Pseudoalteromonas sp. NO3 isolated from the sea squirt Halocynthia rorentzi.
J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36(11) , 1375-82, (2009) Pseudoalteromonas sp. NO3 was isolated from the hemolymph of diseased sea squirts (Halocynthia rorentzi) with symptoms of soft tunic syndrome. The strain was found to produce an extracellular cellulase (CelY) that consisted of a 1,476 bp open reading frame en... |
|
|
Application of the statistical test of equivalent pathways (STEP) method to the triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21(20) , 3365-72, (2007) Recently, we demonstrated a new method, STEP (Statistical Test of Equivalent Pathways) analysis, which differentiates first-generation product ions (primary product ions) from second-generation product ions (secondary product ions) obtained in tandem mass spe... |
|
|
Crystal structure of the rice branching enzyme I (BEI) in complex with maltopentaose.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 424(3) , 508-11, (2012) Starch branching enzyme (SBE) catalyzes the cleavage of α-1,4-linkages and the subsequent transfer of α-1,4 glucan to form an α-1,6 branch point in amylopectin. We determined the crystal structure of the rice branching enzyme I (BEI) in complex with maltopent... |
|
|
Screening and characterization of a cellulase gene from the gut microflora of abalone using metagenomic library.
J. Microbiol. 49(1) , 141-5, (2011) A metagenomic fosmid library was constructed using genomic DNA isolated from abalone intestine. Screening of a library of 3,840 clones revealed a 36 kb insert of a cellulase positive clone (pAMHElO). A shotgun clone library was constructed using the positive ... |