SOYBEAN OIL
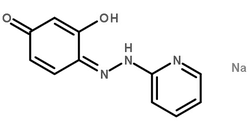
SOYBEAN OIL structure
|
Common Name | SOYBEAN OIL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8001-22-7 | Molecular Weight | 238.19786 | |
| Density | 0.917 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H9N3O2.Na | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | >230 °F | |
|
In vivo effects of polyunsaturated, monounsaturated, and saturated fatty acids on hepatic and peripheral insulin sensitivity.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 64(2) , 315-22, (2015) Free fatty acids (FFAs) cause insulin resistance and are often elevated in obesity. Chronic ingestion of diets rich in saturated fat induces more insulin resistance than diets rich in unsaturated fat, however, it remains unclear whether different FFAs cause d... |
|
|
Preparation of curcumin microemulsions with food-grade soybean oil/lecithin and their cytotoxicity on the HepG2 cell line.
Food Chem. 154 , 282-90, (2014) The choice of surfactants and cosurfactants for preparation of oral formulation in microemulsions is limited. In this report, a curcumin-encapsulated phospholipids-based microemulsion (ME) using food-grade ingredients soybean oil and soybean lecithin to repla... |
|
|
Influence of the type of vegetable oil on the drug release profile from lipid-core nanocapsules and in vivo genotoxicity study.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 19(7) , 789-98, (2014) The use of rice bran (RB), soybean (SB) or sunflower seed (SF) oils to prepare lipid-core nanocapsules (LNCs) as controlled drug delivery systems was investigated. LNCs were prepared by interfacial deposition using the preformed polymer method. All formulatio... |
|
|
Protic ionic liquid as additive on lipase immobilization using silica sol-gel.
Enzyme Microb. Technol. 52(3) , 141-50, (2013) Ionic liquids (ILs) have evolved as a new type of non-aqueous solvents for biocatalysis, mainly due to their unique and tunable physical properties. A number of recent review papers have described a variety of enzymatic reactions conducted in IL solutions, on... |
|
|
The distinct effects of lipid emulsions used for "lipid resuscitation" on gating and bupivacaine-induced inhibition of the cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5.
Anesth. Analg. 117(5) , 1101-8, (2013) Systemic administration of lipid emulsions is an established treatment for local anesthetic intoxication. However, it is unclear by which mechanisms lipids achieve this function. The high cardiac toxicity of the lipophilic local anesthetic bupivacaine probabl... |
|
|
Propofol (Diprivan®) and Intralipid® exacerbate insulin resistance in type-2 diabetic hearts by impairing GLUT4 trafficking.
Anesth. Analg. 120(2) , 329-40, (2015) The IV anesthetic, propofol, when administered as fat emulsion-based formulation (Diprivan) promotes insulin resistance, but the direct effects of propofol and its solvent, Intralipid, on cardiac insulin resistance are unknown.Hearts of healthy and type-2 dia... |
|
|
Intake of farmed Atlantic salmon fed soybean oil increases insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation in mice.
PLoS ONE 8(1) , e53094, (2013) To ensure sustainable aquaculture, fish derived raw materials are replaced by vegetable ingredients. Fatty acid composition and contaminant status of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) are affected by the use of plant ingredients and a spillover effect o... |
|
|
Oxidative stability of soybean oil in oleosomes as affected by pH and iron.
Food Chem. 141(3) , 2286-93, (2013) The oxidative stability of oil in soybean oleosomes, isolated using the Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction Process (EAEP), was evaluated. The effects of ferric chloride, at two concentration levels (100 and 500 μM), on lipid oxidation, was examined under pH 2... |
|
|
Coated kapok fiber for removal of spilled oil.
Mar. Pollut. Bull. 69(1-2) , 91-6, (2013) Based on raw kapok fiber, two kinds of oil absorbers with high sorption capacity were prepared by a facile solution-immersion process. The coated polymer with low surface energy and rough fiber surface play important role in the retention of oil. The as-prepa... |
|
|
Emulsified isoflurane enhances thermal transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 channel activation-mediated sensory/nociceptive blockade by QX-314.
Anesthesiology 121(2) , 280-9, (2014) QX-314 produces nociceptive blockade, facilitated by permeation through transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) channels. TRPV1 channel can be activated by noxious heat and sensitized by volatile anesthetics. The authors hypothesized that emulsified ... |