Creatinine Deiminase
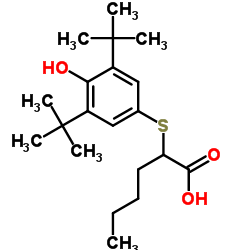
Creatinine Deiminase structure
|
Common Name | Creatinine Deiminase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 37289-15-9 | Molecular Weight | 352.531 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 442.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H32O3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 221.4±28.7 °C | |
|
Amperometric flow-injection analysis of creatinine based on immobilized creatinine deiminase, leucine dehydrogenase and L-amino acid oxidase.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 9(6) , 429-37, (1994) Leucine dehydrogenase/L-amino acid oxidase was proposed as an enzymatic conversion system for ammonia and its application to amperometric assay of creatinine was investigated. Ammonia formed by creatinine deiminase catalyzed hydrolysis of creatinine was conve... |
|
|
Purification and properties of creatinine iminohydrolase from Flavobacterium filamentosum.
J. Biol. Chem. 260(7) , 3915-22, (1985) Creatinine iminohydrolase (EC 3.5.4.21), which catalyzes hydrolysis of creatinine to N-methylhydantoin and ammonia, was purified from Flavobacterium filamentosum. The average molecular weight of the purified enzyme was 272,480, and the subunit molecular weigh... |
|
|
Enzyme kinetic assays with surface plasmon resonance (BIAcore) based on competition between enzyme and creatinine antibody.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 15(7-8) , 377-82, (2000) A procedure is described which allows the characterization of enzyme by a hybrid approach using an enzyme and an antibody. The presented method is related to the affinity determination of antibodies by the 'affinity in solution' procedure for BlAcore. The ant... |
|
|
Biomolecular modules for creatinine determination.
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 799 , 541-4, (1996)
|
|
|
Creatinine deiminase (EC 3.5.4.21) from bacterium BN11: purification, properties and applicability in a serum/urine creatinine assay.
Clin. Chim. Acta 204(1-3) , 223-38, (1991) Creatinine deiminase (EC 3.5.4.21) from the anaerobic microorganism BN11 has been purified to homogeneity by ammonium sulfate fractionation, gel filtration on Sephacryl-S-300 superfine and chromatography on DEAE-Sepharose C1 6B. The final enzyme preparation h... |
|
|
Enzyme rate assay for 5-fluorocytosine.
Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 100(3) , 299-300, (1993) Modification of an enzyme assay for 5-fluorocytosine, from an end point to a rate analysis, has resulted in a method that can provide results within 10 minutes. The modification also rendered the assay less susceptible to interference from bilirubin and trigl... |
|
|
Utilization of creatinine as an alternative nitrogen source in Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Arch. Microbiol. 181(6) , 443-50, (2004) In order to utilize different nitrogen sources and to survive situations of nitrogen limitation, microorganisms have developed several mechanisms to adapt their metabolism to changes in the nitrogen supply. In this communication, the use of creatinine as an a... |
|
|
Calibrationless determination of creatinine and ammonia by coulometric flow titration.
Anal. Biochem. 283(2) , 166-74, (2000) A precise and sensitive working microflow titration procedure was developed to determine creatinine and ammonia in urine samples. This procedure is based on enzymatic conversion of creatinine, gas diffusional membrane separation of the released ammonia into a... |
|
|
Spurious azotemia associated with 5-fluorocytosine therapy.
Urology 36(3) , 283-5, (1990) A patient with false elevation of serum creatinine level due to 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) is reported. 5-FC interferes with the enzymatic method used for creatinine determination in the Kodak Ektachem analyzer. Clinicians should be aware of the potential for sp... |
|
|
Creatinine and N-methylhydantoin degradation in two newly isolated Clostridium species.
Arch. Microbiol. 157(5) , 395-401, (1992) With N-methylhydantoin (NMH) as the main organic substrate, two strictly anaerobic spore forming Gram-positive bacterial strains were isolated from sewage sludge. These strains, named Clostridium sp. FS23 and Clostridium sp. FS41, totally degraded NMH, via N-... |