Aspartate aminotransferase
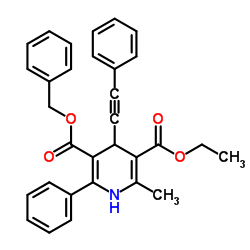
Aspartate aminotransferase structure
|
Common Name | Aspartate aminotransferase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9000-97-9 | Molecular Weight | 477.550 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C | |
|
The effectiveness of fermented turmeric powder in subjects with elevated alanine transaminase levels: a randomised controlled study.
BMC Complement Altern. Med. 13 , 58, (2013) Previous animal studies have shown that Curcuma longa (turmeric) improves liver function. Turmeric may thus be a promising ingredient in functional foods aimed at improving liver function. The purpose of the study is to investigate the hepatoprotective effect... |
|
|
Does liver damage explain the inverse association between vitamin D status and mortality?
Ann. Epidemiol. 23(12) , 812-4, (2013) Several observational studies have linked vitamin D deficiency with an increased risk of all cause mortality. Vitamin D deficiency is common among patients with liver diseases. In a random sample of the general population, we investigated whether the inverse ... |
|
|
Plasma level of atherogenic and anti-atherogenic factors among palm wine drinkers of rural southwest Nigeria.
Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 41(4) , 337-47, (2012) Scientific evidence indicates that light to moderate drinking on a daily basis may significantly reduce the risks of coronary heart disease (CHD). In contrast, excessive alcohol intake and binge drinking are toxic to both the heart and overall health. There i... |
|
|
[Effect of cordyceps polysaccharide on lipid peroxidation of rats with dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(3) , 391-6, (2013) To observe the pharmacological effect of Cordyceps polysaccharide on dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rats.DMN rat liver fibrosis model was established and divided into the normal group (N, n = 6), the model group (M, n = 11), the Cordyceps... |
|
|
Association between histological findings, aminotransferase levels and viral genotype in chronic hepatitis C infection.
Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 47(1) , 90-2, (2014) The genomic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus (HCV) influences liver disorders. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of HCV genotypes and to investigate the influence of these genotypes on disease progression.Blood samples and liver biopsies were col... |
|
|
Etiology and epidemiology of obstructive jaundice in Continental Croatia.
Coll. Antropol. 37(1) , 131-3, (2013) The etiology and epidemiology of obstructive jaundice in Continental Croatia has been studied in 174 patients. The objective of this research was also to explore the importance and efficiency of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) as a non-s... |
|
|
Initial characterization of the human central proteome.
BMC Syst. Biol. 5 , 17, (2011) On the basis of large proteomics datasets measured from seven human cell lines we consider their intersection as an approximation of the human central proteome, which is the set of proteins ubiquitously expressed in all human cells. Composition and properties... |
|
|
Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.
Nat. Genet. 36 , 40-5, (2004) As a base for human transcriptome and functional genomics, we created the "full-length long Japan" (FLJ) collection of sequenced human cDNAs. We determined the entire sequence of 21,243 selected clones and found that 14,490 cDNAs (10,897 clusters) were unique... |
|
|
The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).
Genome Res. 14 , 2121-7, (2004) The National Institutes of Health's Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) project was designed to generate and sequence a publicly accessible cDNA resource containing a complete open reading frame (ORF) for every human and mouse gene. The project initially used a r... |
|
|
Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions.
Science 325(5942) , 834-40, (2009) Lysine acetylation is a reversible posttranslational modification of proteins and plays a key role in regulating gene expression. Technological limitations have so far prevented a global analysis of lysine acetylation's cellular roles. We used high-resolution... |