CNQX
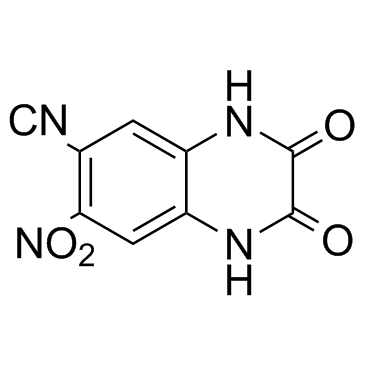
CNQX structure
|
Common Name | CNQX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 115066-14-3 | Molecular Weight | 232.152 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 659.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H4N4O4 | Melting Point | 300 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 352.6ºC | |
|
Glutamatergic receptor dysfunction in spinal cord contributes to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in heart failure.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308(5) , H447-55, (2015) Excitatory amino acids (e.g., glutamate) released by contraction-activated skeletal muscle afferents into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord initiate the central component of the exercise pressor reflex (EPR) in physiological conditions. However, the role of ... |
|
|
Nitrous oxide directly inhibits action potential-dependent neurotransmission from single presynaptic boutons adhering to rat hippocampal CA3 neurons.
Brain Res. Bull. 118 , 34-45, (2015) We evaluated the effects of N2O on synaptic transmission using a preparation of mechanically dissociated rat hippocampal CA3 neurons that allowed assays of single bouton responses evoked from native functional nerve endings. We studied the effects of N2O on G... |
|
|
HD iPSC-derived neural progenitors accumulate in culture and are susceptible to BDNF withdrawal due to glutamate toxicity.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 24 , 3257-71, (2015) Huntington's disease (HD) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease, caused by expansion of polyglutamine repeats in the Huntingtin gene, with longer expansions leading to earlier ages of onset. The HD iPSC Consortium has recently reported a new in vitro model of ... |
|
|
Store-operated calcium entry compensates fast ER calcium loss in resting hippocampal neurons.
Cell Calcium 58 , 147-59, (2015) The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) acts as a dynamic calcium store and is involved in the generation of specific patterns of calcium signals in neurons. Calcium is mobilized from the ER store by multiple signaling cascades, and neuronal activity is known to regul... |
|
|
Modulation of nociceptive dural input to the trigeminocervical complex through GluK1 kainate receptors.
Pain 156(3) , 439-50, (2015) Migraine is a common and disabling neurologic disorder, with important psychiatric comorbidities. Its pathophysiology involves activation of neurons in the trigeminocervical complex (TCC). Kainate receptors carrying the glutamate receptor subunit 5 (GluK1) ar... |
|
|
Anatomical and electrophysiological changes in striatal TH interneurons after loss of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway.
Brain Struct. Funct. 220(1) , 331-49, (2015) Using transgenic mice that express enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) under the control of the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter, we have previously shown that there are approximately 3,000 striatal EGFP-TH interneurons per hemisphere in mice. Here, w... |
|
|
Cholinergic control of gamma power in the midbrain spatial attention network.
J. Neurosci. 35(2) , 761-75, (2015) The modulation of gamma power (25-90 Hz) is associated with attention and has been observed across species and brain areas. However, mechanisms that control these modulations are poorly understood. The midbrain spatial attention network in birds generates hig... |
|
|
Curtailing effect of awakening on visual responses of cortical neurons by cholinergic activation of inhibitory circuits.
J. Neurosci. 34(30) , 10122-33, (2014) Visual responsiveness of cortical neurons changes depending on the brain state. Neural circuit mechanism underlying this change is unclear. By applying the method of in vivo two-photon functional calcium imaging to transgenic rats in which GABAergic neurons e... |
|
|
Pathophysiological mechanisms underlying increased anxiety after soman exposure: reduced GABAergic inhibition in the basolateral amygdala.
Neurotoxicology 44 , 335-43, (2014) The recent sarin attack in Syria killed 1429 people, including 426 children, and left countless more to deal with the health consequences of the exposure. Prior to the Syrian chemical assault, nerve agent attacks in Japan left many victims suffering from neur... |
|
|
Effects of tramadol on substantia gelatinosa neurons in the rat spinal cord: an in vivo patch-clamp analysis.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0125147, (2015) Tramadol is thought to modulate synaptic transmissions in the spinal dorsal horn mainly by activating µ-opioid receptors and by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamines in the CNS. However, the precise mode of modulation remains unclear. We used an in vivo patch... |