Ethyl hydroxycarbamate
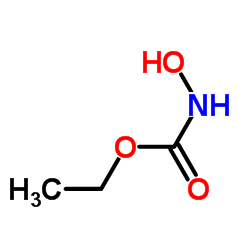
Ethyl hydroxycarbamate structure
|
Common Name | Ethyl hydroxycarbamate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 589-41-3 | Molecular Weight | 105.093 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 254.2±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 107.5±18.7 °C | |
|
Enhanced antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles obtained by electrochemical synthesis in poly(amide-hydroxyurethane) media.
J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22(4) , 789-96, (2011) In the present study, we report enhanced antimicrobial properties of 29 and 23 nm silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) obtained by electrochemical synthesis in poly(amide-hydroxyurethane) media. Antibacterial activity assessed by disk diffusion method indicates that... |
|
|
Induction of chromosome breaks in cultured normal human leukocytes by potassium arsenite, hydroxyurea and related compounds.
Cancer Res. 25(7) , 980-5, (1965)
|
|
|
Antiteratogenic effects of tumor inhibitors, caffeine, antipain, and retinoic acid in mice.
Cancer Res. 43(11) , 5156-62, (1983) To learn the effects of tumor inhibitors on chemically induced malformations, caffeine, antipain, and 13-trans-retinoic acid were given to pregnant ICR/Jcl mice after a single dose of urethan, N-hydroxyurethan, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea, N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea, o... |
|
|
Timing of chemically induced neoplasia in mice revealed by the antineoplastic action of caffeine.
Cancer Res. 40(4) , 1332-40, (1980)
|
|
|
Comparative carcinogenicities and mutagenicities of vinyl carbamate, ethyl carbamate, and ethyl N-hydroxycarbamate.
Cancer Res. 40(4) , 1194-203, (1980)
|
|
|
DNA repair synthesis induced by N-hydroxyurea, acetohydroxamic acid, and N-hydroxyurethane in primary rat hepatocyte cultures: comparative evaluation using the autoradiographic and the bromodeoxyuridine density-shift method.
Mutat. Res. 145(3) , 201-7, (1985) N-Hydroxyurea and two structurally related compounds, acetohydroxamic acid and N-hydroxyurethane, were investigated for their potential to induce DNA repair synthesis in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. Repair was determined as repair replication by means of ... |
|
|
Rodent species and strain specificities for sister-chromatid exchange induction and gene mutagenesis effects from ethyl carbamate, ethyl N-hydroxycarbamate, and vinyl carbamate.
Mutat. Res. 126(2) , 159-67, (1984) Ethyl carbamate (EC) and two related carcinogens, ethyl N-hydroxycarbamate (ENHC) and vinyl carbamate (VC), caused species-specific increases in sister-chromatid exchange (SCE) formation in the bone marrow cells of rodents. Mice exposed to 400 mg/kg of EC had... |
|
|
Involvement of liver aldehyde oxidase in conversion of N-hydroxyurethane to urethane.
J. Pharmacobiodyn. 6(9) , 677-83, (1983) The present study provides the evidence that liver aldehyde oxidase in the presence of its electron donors can catalyze the reduction of N-hydroxyurethane to urethane under anaerobic conditions. Guinea pig liver 9000 X g supernatant and cytosol, but not liver... |
|
|
Immunotoxicity of ethyl carbamate in female BALB/c mice: role of esterase and cytochrome P450.
Toxicol. Lett. 115(3) , 173-81, (2000) Ethyl carbamate, a potent carcinogen, has been characterized to be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (P450) and esterase. It has recently been demonstrated that P450 may activate ethyl carbamate to immunotoxic metabolites. To investigate the role of esterase in ... |
|
|
Metabolism of carcinogenic urethane to nitric oxide is involved in oxidative DNA damage.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33(5) , 703-14, (2002) Carcinogenic urethane (ethyl carbamate) forms DNA adduct via epoxide, whereas carcinogenic methyl carbamate can not. To clarify a mechanism independent of DNA adduct formation, we examined DNA damage induced by N-hydroxyurethane, a urethane metabolite, using ... |