Tubacin
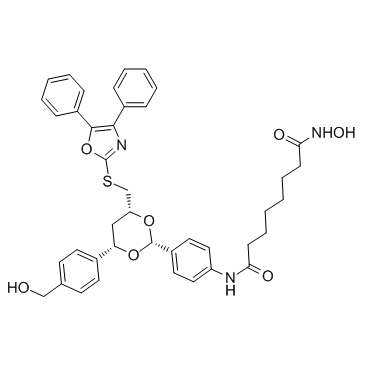
Tubacin structure
|
Common Name | Tubacin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 537049-40-4 | Molecular Weight | 721.861 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C41H43N3O7S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
SMAR1 coordinates HDAC6-induced deacetylation of Ku70 and dictates cell fate upon irradiation.
Cell Death Dis. 5 , e1447, (2014) Acetylation status of DNA end joining protein Ku70 dictates its function in DNA repair and Bax-mediated apoptosis. Despite the knowledge of HDACs and HATs that are reported to modulate the acetylation dynamics of Ku70, very little is known about proteins that... |
|
|
Limited efficacy of specific HDAC6 inhibition in urothelial cancer cells.
Cancer Biol. Ther. 15(6) , 742-57, (2014) Epigenetic modifiers such as histone deacetylases (HDACs) have come into focus as novel drug targets for cancer therapy due to their functional role in tumor progression. Since common pan-HDAC inhibitors have adverse side effects and minor anti-cancer activit... |
|
|
Syntheses and discovery of a novel class of cinnamic hydroxamates as histone deacetylase inhibitors by multimodality molecular imaging in living subjects.
Cancer Res. 74(24) , 7475-86, (2014) Histone deacetylases (HDAC) that regulate gene expression are being explored as cancer therapeutic targets. In this study, we focused on HDAC6 based on its ability to inhibit cancerous Hsp90 chaperone activities by disrupting Hsp90/p23 interactions. To identi... |
|
|
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Repress Tumoral Expression of the Proinvasive Factor RUNX2.
Cancer Res. 75 , 1868-82, (2015) Aberrant reactivation of embryonic pathways occurs commonly in cancer. The transcription factor RUNX2 plays a fundamental role during embryogenesis and is aberrantly reactivated during progression and metastasization of different types of human tumors. In thi... |
|
|
Inhibiting histone deacetylase 6 partly protects cultured rat cortical neurons from oxygen‑glucose deprivation‑induced necroptosis.
Mol. Med. Report. 12 , 2661-7, (2015) Necroptosis has an important role in ischemia-reperfusion damage. The expression of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is upregulated in neurons following ischemia-reperfusion, however, whether HDAC6 is closely involved in the necroptosis, which occurs during isch... |
|
|
Tubacin prevents neuronal migration defects and epileptic activity caused by rat Srpx2 silencing in utero.
Brain 136(Pt 8) , 2457-73, (2013) Altered development of the human cerebral cortex can cause severe malformations with often intractable focal epileptic seizures and may participate in common pathologies, notably epilepsy. This raises important conceptual and therapeutic issues. Two missense ... |
|
|
Tubacin kills Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-Burkitt lymphoma cells by inducing reactive oxygen species and EBV lymphoblastoid cells by inducing apoptosis.
J. Biol. Chem. 284 , 17102-17109, (2009) Tubacin is a small molecule inhibitor of histone deacetylase 6 and blocks aggresome activity. We found that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive Burkitt lymphoma (BL) cells were generally killed by lower doses of tubacin than EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cells... |
|
|
HDAC6 and SIRT2 promote bladder cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting cortactin.
Oncol. Rep. 27(3) , 819-24, (2012) Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) promotes cell motility and contributes to the metastasis of cancers. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of HDAC6 in human bladder cancer for the first time. The results showed that HDAC6 promotes the migration ... |
|
|
Tubacin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.
Leukemia Lymphoma 52 , 1544-1555, (2011) Over the past decade, histone deacetylase inhibitors have increasingly been used to treat various malignancies. Tubacin (tubulin acetylation inducer) is a small molecule that inhibits histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and induces acetylation of α-tubulin. We obse... |
|
|
HDAC6 Promotes Cardiac Fibrosis Progression through Suppressing RASSF1A Expression.
Cardiology 133 , 18-26, (2015) Cardiac fibrosis is characterized by net accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins in the cardiac interstitium, and contributes to both systolic and diastolic dysfunction in many cardiac pathophysiologic conditions. HDAC6 is a transcriptional regulator of... |