Cinnabarinic acid
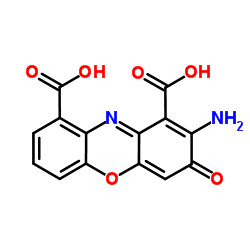
Cinnabarinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Cinnabarinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 606-59-7 | Molecular Weight | 300.223 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 536.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O6 | Melting Point | >300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 278.4±30.1 °C | |
|
Aminophenoxazinones as inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Synthesis of exfoliazone and chandrananimycin A.
J. Med. Chem. 56(8) , 3310-7, (2013) A range of 2-aminophenoxazin-3-ones has been prepared by oxidative cyclocondensation of 2-aminophenols, including the natural products exfoliazone and chandrananimycin A, both synthesized for the first time. The compounds were evaluated for their ability to i... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of 3-hydroxyanthranilic and cinnabarinic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography with photometric or electrochemical detection.
Anal. Biochem. 200(2) , 273-9, (1992) A convenient and rapid method for the simultaneous determination by HPLC of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid and the dimer derived by its oxidation, cinnabarinic acid, is described. Buffers or biological samples containing these two Trp metabolites were acidified to... |
|
|
Oxidation of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid to the phenoxazinone cinnabarinic acid by peroxyl radicals and by compound I of peroxidases or catalase.
Biochemistry 31(34) , 8090-7, (1992) Since 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (3HAA), an oxidation product of tryptophan metabolism, is a powerful radical scavenger [Christen, S., Peterhans, E., & Stocker, R. (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 2506], its reaction with peroxyl radicals was investiga... |
|
|
Mechanism of reaction of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid with molecular oxygen.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1034(2) , 207-12, (1990) The autoxidation of the tryptophan metabolite, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid, at pH 7 gives rise to a p-quinone dimer and cinnabarinic acid. A novel dimer formed by radical-radical coupling of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid is also produced. Labelling studies have sho... |
|
|
Oxidative reactivity of the tryptophan metabolites 3-hydroxyanthranilate, cinnabarinate, quinolinate and picolinate.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 36(2) , 211-7, (1987) The oxidative reactivities of four tryptophan metabolites in the kynurenine pathway were examined as a potential mechanism for their reported neurotoxicities and carcinogenicities. Neither quinolinic acid, a neurotoxin, nor its monocarboxylic analogue, picoli... |
|
|
Novel interaction between laccase and cellobiose dehydrogenase during pigment synthesis in the white rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65(2) , 389-95, (1999) When glucose is the carbon source, the white rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus produces a characteristic red pigment, cinnabarinic acid, which is formed by laccase-catalyzed oxidation of the precursor 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid. When P. cinnabarinus was grown... |
|
|
Laccase-mediated formation of the phenoxazinone derivative, cinnabarinic acid.
FEBS Lett. 376(3) , 202-6, (1995) The phenoxazinone chromophore occurs in a variety of biological systems, including numerous pigments and certain antibiotics. It also appears to form as part of a mechanism to protect mammalian tissue from oxidative damage. During cultivation of the basidiomy... |
|
|
Cinnabarinate formation in malpighian tubules of the silkworm. Bombyx mori: reaction mechanism of cinnabarinate formation in the presence of catalase and manganese ions.
Hoppe. Seylers. Z. Physiol. Chem. 364(11) , 1507-18, (1983) The formation of cinnabarinate in the presence of manganese ions and catalase was investigated spectrophotometrically. The absorption peak of cinnabarinate at 460 nm appeared only in a reaction system containing manganese ions and catalase. If catalase was om... |
|
|
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid-derived compounds formed through electrochemical oxidation.
J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 736(1-2) , 237-45, (1999) 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-HAA)-derived oxidation products were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography with an electrochemical reactor and diode array detection and high-performance liquid chromatography with an electrochemical reactor and UV... |
|
|
Superoxide dismutase enhances the formation of hydroxyl radicals in the reaction of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid with molecular oxygen.
Biochem. J. 251(3) , 893-9, (1988) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) enhanced the formation of hydroxyl radicals, which were detected by using the e.s.r. spin-trapping technique, in a reaction mixture containing 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (or p-aminophenol), Fe3+ ions, EDTA and potassium phosphate buf... |