4-Fluoro-Phe-OH
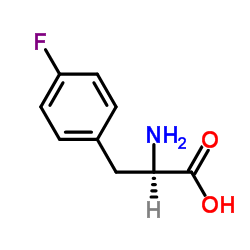
4-Fluoro-Phe-OH structure
|
Common Name | 4-Fluoro-Phe-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1132-68-9 | Molecular Weight | 183.180 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 313.3±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10FNO2 | Melting Point | ~255 °C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 143.3±25.1 °C | |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Regulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. I. Kinetic properties of the enzyme's iron and enzyme reduction site.
J. Biol. Chem. 269 , 24637, (1994) Tetrahydropterins react with phenylalanine hydroxylase at a redox site, a regulatory site, and the catalytic site, but neither the properties of nor relationships among these sites are well understood. We have studied the redox site using the fluorescent iron... |
|
|
A mechanism for hydroxylation by tyrosine hydroxylase based on partitioning of substituted phenylalanines.
Biochemistry 35 , 6969, (1996) The iron-containing enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the hydroxylation of tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalanine. A series of 4-X-substituted (X = H, F, Br, Cl, CH3, or CH3O) phenylalanines have been characterized as substrates to gain insight into the mecha... |
|
|
Chromosome condensing ability of mitotic proteins diminished by the substitution of phenylalanine with parafluorophenylalanine.
Eur. J. Cell Biol. 23 , 312-316, (1981) One of the objectives of this study was to develop a method for the reversible arrest of HeLa cells in G2 phase by using p-fluorophenylalanine (FPA), an analog of phenylalanine. Addition of 0.5 mM of FPA to synchronized HeLa cells during the middle of S phase... |