KN-93
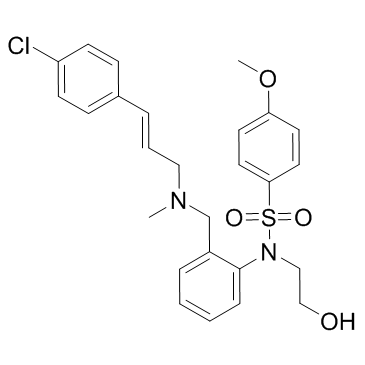
KN-93 structure
|
Common Name | KN-93 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 139298-40-1 | Molecular Weight | 501.038 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 657.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H29ClN2O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 351.5±34.3 °C | |
|
Ca(2+) permeation and/or binding to CaV1.1 fine-tunes skeletal muscle Ca(2+) signaling to sustain muscle function.
Skelet. Muscle 5 , 4, (2015) Ca(2+) influx through CaV1.1 is not required for skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling, but whether Ca(2+) permeation through CaV1.1 during sustained muscle activity plays a functional role in mammalian skeletal muscle has not been assessed.We gener... |
|
|
Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 1 (TRPC1) Channels as Regulators of Sphingolipid and VEGF Receptor Expression: IMPLICATIONS FOR THYROID CANCER CELL MIGRATION AND PROLIFERATION.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 16116-31, (2015) The identity of calcium channels in the thyroid is unclear. In human follicular thyroid ML-1 cancer cells, sphingolipid sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), through S1P receptors 1 and 3 (S1P1/S1P3), and VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) stimulates migration. We show that h... |
|
|
Modulation of P2X4/P2X7/Pannexin-1 sensitivity to extracellular ATP via Ivermectin induces a non-apoptotic and inflammatory form of cancer cell death.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 16222, (2015) Overexpression of P2X7 receptors correlates with tumor growth and metastasis. Yet, release of ATP is associated with immunogenic cancer cell death as well as inflammatory responses caused by necrotic cell death at sites of trauma or ischemia-reperfusion injur... |
|
|
Intracellular Na+ overload causes oxidation of CaMKII and leads to Ca2+ mishandling in isolated ventricular myocytes.
J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 76 , 247-56, (2014) An increase of late Na(+) current (INaL) in cardiac myocytes can raise the cytosolic Na(+) concentration and is associated with activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and alterations of mitochondrial metabolism and Ca(2+) handlin... |
|
|
Calcium Signaling Is Required for Erythroid Enucleation.
PLoS ONE 11 , e0146201, (2016) Although erythroid enucleation, the property of erythroblasts to expel their nucleus, has been known for 7ore than a century, surprisingly little is known regarding the molecular mechanisms governing this unique developmental process. Here we show that simila... |
|
|
Activation of Phosphatidylinositol-Linked Dopamine Receptors Induces a Facilitation of Glutamate-Mediated Synaptic Transmission in the Lateral Entorhinal Cortex.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0131948, (2015) The lateral entorhinal cortex receives strong inputs from midbrain dopamine neurons that can modulate its sensory and mnemonic function. We have previously demonstrated that 1 µM dopamine facilitates synaptic transmission in layer II entorhinal cortex cells v... |
|
|
Mitochondrial oxidative stress promotes atrial fibrillation.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 11427, (2015) Oxidative stress has been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation (AF). Indeed, the prevalence of AF increases with age as does oxidative stress. However, the mechanisms linking redox state to AF are not well understood. In this st... |
|
|
The growth and aggressive behavior of human osteosarcoma is regulated by a CaMKII-controlled autocrine VEGF signaling mechanism.
PLoS ONE 10(4) , e0121568, (2015) Osteosarcoma (OS) is a hyperproliferative malignant tumor that requires a high vascular density to maintain its large volume. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) plays a crucial role in angiogenesis and acts as a paracrine and autocrine agent affecting ... |
|
|
Integrated Transcriptional and Proteomic Analysis of Growth Hormone Suppression Mediated by Trichothecene T-2 Toxin in Rat GH3 Cells.
Toxicol. Sci. 147 , 326-38, (2015) Chronic exposure to trichothecenes is known to disturb insulin-like growth factor 1 and signaling of insulin and leptin hormones and causes considerable growth retardation in animals. However, limited information was available on mechanisms underlying trichot... |
|
|
Epac is required for GLP-1R-mediated inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes.
Mol. Endocrinol. 29(4) , 583-96, (2015) Although the cardioprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and its analogs have been reported, the exact mechanisms of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) signaling pathway in the heart are still unclear. Activation of the GLP-1R has been show... |