4-Nitrophenyl Laurate
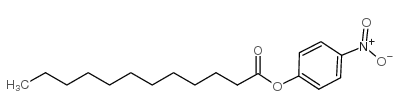
4-Nitrophenyl Laurate structure
|
Common Name | 4-Nitrophenyl Laurate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1956-11-2 | Molecular Weight | 321.41 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H27NO4 | Melting Point | ~46 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Structural insights into methanol-stable variants of lipase T6 from Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 9449-61, (2015) Enzymatic production of biodiesel by transesterification of triglycerides and alcohol, catalyzed by lipases, offers an environmentally friendly and efficient alternative to the chemically catalyzed process while using low-grade feedstocks. Methanol is utilize... |
|
|
Biochemistry of lipolytic enzymes secreted by Penicillium solitum and Cladosporium cladosporioides.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 78(2) , 245-54, (2014) Two distinct extracellular lipases were obtained from Penicillium solitum 194A, isolated from domestic compost, and Cladosporium cladosporioides 194B, isolated from dairy wastewater. These alkaline enzymes had molecular masses of 42 and 30 kDa, respectively. ... |
|
|
Expression and properties of three novel fungal lipases/sterol esterases predicted in silico: comparison with other enzymes of the Candida rugosa-like family.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 , 10057-67, (2015) Lipases from the Candida rugosa-like family are enzymes with great biotechnological interest. In a previous work, several enzymes from this family were identified by in silico mining of fungal genomes. Here, we describe the cloning, expression, and characteri... |
|
|
Harmaline and hispidin from Peganum harmala and Inonotus hispidus with binding affinity to Candida rugosa lipase: In silico and in vitro studies.
Bioorg. Chem. 62 , 1-7, (2015) The inhibitory effect of phenolic compounds and alkaloids of Inonotus hispidus and Peganum harmala on Candida rugosa lipase was investigated, also, their antioxidant activities using DPPH, ABTS and phosphomolybdenum were studied in this paper. The phenolic ex... |
|
|
Characterization of an acidic cold-adapted cutinase from Thielavia terrestris and its application in flavor ester synthesis.
Food Chem. 188 , 439-45, (2015) An acidic cutinase (TtcutB) from Thielavia terrestris CAU709 was purified to apparent homogeneity with 983 Um g(-1) specific activity. The molecular mass of the enzyme was estimated to be 27.3 and 27.9 kDa by SDS-PAGE and gel filtration, respectively. A pepti... |
|
|
A novel alkaliphilic bacillus esterase belongs to the 13(th) bacterial lipolytic enzyme family.
PLoS ONE 8 , e60645, (2013) Microbial derived lipolytic hydrolysts are an important class of biocatalysts because of their huge abundance and ability to display bioactivities under extreme conditions. In spite of recent advances, our understanding of these enzymes remains rudimentary. T... |
|
|
Biochemical characterization of a first fungal esterase from Rhizomucor miehei showing high efficiency of ester synthesis.
PLoS ONE 8 , e77856, (2013) Esterases with excellent merits suitable for commercial use in ester production field are still insufficient. The aim of this research is to advance our understanding by seeking for more unusual esterases and revealing their characterizations for ester synthe... |
|
|
Identification of extracellular lipases/esterases produced by Thermus thermophilus HB27: partial purification and preliminary biochemical characterisation.
J. Biotechnol. 117(3) , 233-41, (2005) Thermus thermophilus HB27 produces important levels of extracellular lipolytic activity when grown for 30 h at 70 degrees C in a complex medium. A method to detect esterase activity in these samples after non-reducing SDS-polyacrylamide electrophoresis was de... |
|
|
Production of thermostable lipolytic activity by thermus species.
Biotechnol. Prog. 21(4) , 1198-205, (2005) A quantitative screening for intra- and extracellular lipolytic activity was performed in submerged cultures of four Thermus strains using two different media (named T or D medium). Major differences in the extracellular lipolytic activity were observed in T ... |
|
|
Interfacial reaction dynamics and acyl-enzyme mechanism for lipoprotein lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of lipid p-nitrophenyl esters.
J. Biol. Chem. 261(26) , 12016-21, (1986) The fatty acyl (lipid) p-nitrophenyl esters p-nitrophenyl caprylate, p-nitrophenyl laurate and p-nitrophenyl palmitate that are incorporated at a few mol % into mixed micelles with Triton X-100 are substrates for bovine milk lipoprotein lipase. When the conce... |