NSC 204421
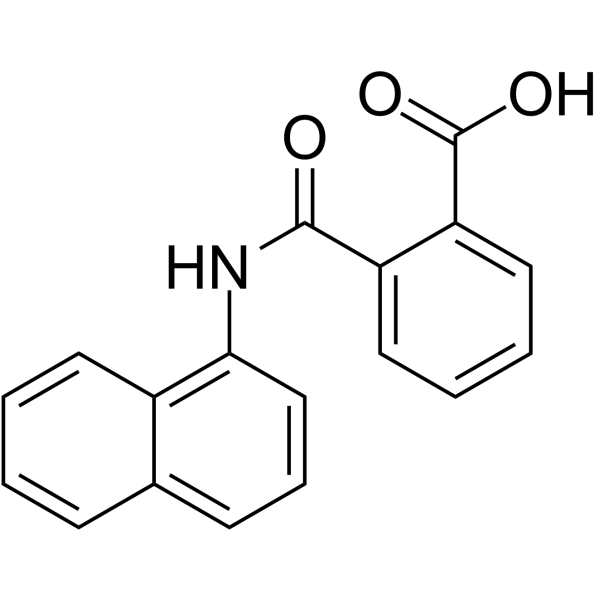
NSC 204421 structure
|
Common Name | NSC 204421 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 132-66-1 | Molecular Weight | 291.30 | |
| Density | 1.355g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 450.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H13NO3 | Melting Point | 185-190 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 226.4ºC | |
|
Non-invasive quantification of endogenous root auxin transport using an integrated flux microsensor technique.
Plant J. 63(6) , 1004-16, (2010) Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) is a primary phytohormone that regulates multiple aspects of plant development. Because polar transport of IAA is an essential determinant of organogenesis and dynamic tropic growth, methods to monitor IAA movement in vivo are in de... |
|
|
Auxin modulates the enhanced development of root hairs in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. under elevated CO(2).
Plant Cell Environ. 34(8) , 1304-17, (2011) Root hairs may play a critical role in nutrient acquisition of plants grown under elevated CO(2) . This study investigated how elevated CO(2) enhanced the development of root hairs in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. The plants under elevated CO(2) (800 µL L(... |
|
|
Expression profile of PIN, AUX/LAX and PGP auxin transporter gene families in Sorghum bicolor under phytohormone and abiotic stress.
FEBS J. 277 , 2954-2969, (2010) Auxin is transported by the influx carriers auxin resistant 1/like aux1 (AUX/LAX), and the efflux carriers pin-formed (PIN) and P-glycoprotein (PGP), which play a major role in polar auxin transport. Several auxin transporter genes have been characterized in ... |
|
|
Identification of IAA transport inhibitors including compounds affecting cellular PIN trafficking by two chemical screening approaches using maize coleoptile systems.
Plant Cell Physiol. 53(10) , 1671-82, (2012) The monocot coleoptile tip region has been generally supposed to be the source of IAA to supply IAA to basal parts by the polar IAA transport system, which results in gravi- and phototropic curvature of coleoptiles. Based on this IAA transport system and grav... |
|
|
Chemical stimulation of the Arabidopsis thaliana root using multi-laminar flow on a microfluidic chip.
Lab Chip 10(16) , 2147-53, (2010) In this article, we developed a "plant on a chip" microfluidic platform that can control the local chemical environment around live roots of Arabidopsis thaliana with high spatial resolution using multi-laminar flow. We characterized the flow profile around t... |
|
|
Pseudonodule formation by wild-type and symbiotic mutant Medicago truncatula in response to auxin transport inhibitors.
Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 24(11) , 1372-84, (2011) Rhizobium and allied bacteria form symbiotic nitrogen-fixing nodules on legume roots. Plant hormones play key roles in nodule formation. We treated Medicago truncatula roots with auxin transport inhibitors (ATI) N-(1-naphthyl)phthalamic acid (NPA) and 2,3,5-t... |
|
|
Rice develop wavy seminal roots in response to light stimulus.
Plant Cell Rep. 30(9) , 1747-58, (2011) Rice (Oryza sativa L.) seminal roots are the primary roots to emerge from germinated seeds. Here, we demonstrate that the photomorphology of the seminal roots was diverse among rice varieties, and the light-induced wavy roots were found mostly in indica-type ... |
|
|
Comparative expression pattern analysis of WUSCHEL-related homeobox 2 (WOX2) and WOX8/9 in developing seeds and somatic embryos of the gymnosperm Picea abies.
New Phytol. 188(1) , 122-35, (2010) • In seed plants, current knowledge concerning embryonic pattern formation by polar auxin transport (PAT) and WUSCHEL-related homeobox (WOX) gene activity is primarily derived from studies on angiosperms, while less is known about these processes in gymnosper... |
|
|
The putative auxin efflux carrier OsPIN3t is involved in the drought stress response and drought tolerance.
Plant J. 72(5) , 805-16, (2012) The phytohormone auxin plays a critical role in plant growth and development, and its spatial distribution largely depends on the polar localization of the PIN-FORMED (PIN) auxin efflux carrier family members. In this study, we identify a putative auxin efflu... |
|
|
Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 in β-cyclodextrin-hemin complex-induced cucumber adventitious rooting process.
Plant Cell Rep. 31(9) , 1563-72, (2012) Our previous results showed that β-cyclodextrin-hemin complex (CDH) exhibited a vital protective role against cadmium-induced oxidative damage and toxicity in alfalfa seedling roots by the regulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) gene expression. In this report,... |