Mupirocin
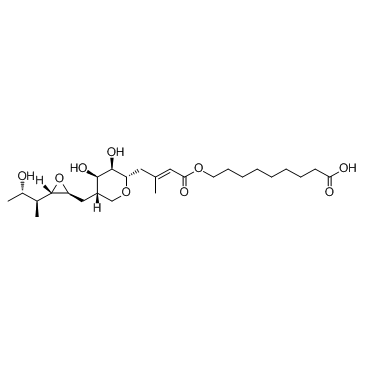
Mupirocin structure
|
Common Name | Mupirocin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 12650-69-0 | Molecular Weight | 500.622 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 672.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H44O9 | Melting Point | 77-780C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.5±25.0 °C | |
|
Purification and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacillithiol transferase BstA.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(9) , 2851-61, (2014) Gram-positive bacteria in the phylum Firmicutes synthesize the low molecular weight thiol bacillithiol rather than glutathione or mycothiol. The bacillithiol transferase YfiT from Bacillus subtilis was identified as a new member of the recently discovered Din... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Simultaneous monitoring of Staphylococcus aureus growth in a multi-parametric microfluidic platform using microscopy and impedance spectroscopy.
Bioelectrochemistry 105 , 56-64, (2015) We describe the design, construction, and characterization of a scalable microfluidic platform that allows continuous monitoring of biofilm proliferation under shear stress conditions. Compared to other previous end-point assay studies, our platform offers th... |
|
|
Short-term decline in all-cause acquired infections with the routine use of a decontamination regimen combining topical polymyxin, tobramycin, and amphotericin B with mupirocin and chlorhexidine in the ICU: a single-center experience.
Crit. Care Med. 42(5) , 1121-30, (2014) In a multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind trial, we showed that acquired infections in intubated patients were reduced by the combination of topical polymyxin plus tobramycin and nasal mupirocin plus chlorhexidine body wash. Because intub... |
|
|
Prevalence of chlorhexidine-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus following prolonged exposure.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(8) , 4404-10, (2014) Chlorhexidine has been increasingly utilized in outpatient settings to control methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) outbreaks and as a component of programs for MRSA decolonization and prevention of skin and soft-tissue infections (SSTIs). The o... |
|
|
LL-37-derived peptides eradicate multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from thermally wounded human skin equivalents.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(8) , 4411-9, (2014) Burn wound infections are often difficult to treat due to the presence of multidrug-resistant bacterial strains and biofilms. Currently, mupirocin is used to eradicate methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from colonized persons; however, mupiroc... |
|
|
The Use of Liprotides To Stabilize and Transport Hydrophobic Molecules.
Biochemistry 54 , 4815-23, (2015) Recently, it has been shown that different complexes consisting of protein and fatty acids, which we call liprotides, have common functional and structural features. Liprotides can transfer their fatty acid content to membranes, highlighting the potential to ... |
|
|
Silencing of Essential Genes within a Highly Coordinated Operon in Escherichia coli.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 5650-9, (2015) Essential bacterial genes located within operons are particularly challenging to study independently because of coordinated gene expression and the nonviability of knockout mutants. Essentiality scores for many operon genes remain uncertain. Antisense RNA (as... |
|
|
Oral antibiotics versus topical decolonization to prevent surgical site infection after Mohs micrographic surgery--a randomized, controlled trial.
Dermatol. Surg. 39(10) , 1486-93, (2013) The optimal method of reducing the risk of surgical site infection (SSI) after dermatologic surgery is unclear. Empiric, preoperative antibiotic use is common practice but lacks supporting evidence for its efficacy in preventing SSI. Risk stratification for p... |
|
|
Screening for MRSA and isolating carriers doesn't reduce ICU infections.
BMJ 346 , f3581, (2013)
|