Temsirolimus (CCI-779)
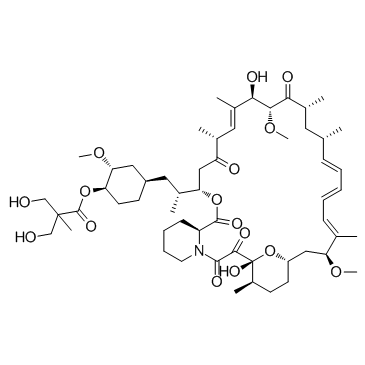
Temsirolimus (CCI-779) structure
|
Common Name | Temsirolimus (CCI-779) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 162635-04-3 | Molecular Weight | 1030.287 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1048.4±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C56H87NO16 | Melting Point | 99-101ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 587.8±37.1 °C | |
|
Che-1-induced inhibition of mTOR pathway enables stress-induced autophagy.
EMBO J. 34 , 1214-30, (2015) Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a key protein kinase that regulates cell growth, metabolism, and autophagy to maintain cellular homeostasis. Its activity is inhibited by adverse conditions, including nutrient limitation, hypoxia, and DNA damage. In th... |
|
|
Dual fatty acid synthase and HER2 signaling blockade shows marked antitumor activity against breast cancer models resistant to anti-HER2 drugs.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0131241, (2015) Blocking the enzyme Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN) leads to apoptosis of HER2-positive breast carcinoma cells. The hypothesis is that blocking FASN, in combination with anti-HER2 signaling agents, would be an effective antitumor strategy in preclinical HER2+ brea... |
|
|
Dual blockade of PI3K/AKT/mTOR (NVP-BEZ235) and Ras/Raf/MEK (AZD6244) pathways synergistically inhibit growth of primary endometrioid endometrial carcinoma cultures, whereas NVP-BEZ235 reduces tumor growth in the corresponding xenograft models.
Gynecol. Oncol. 138 , 165-73, (2015) Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is the most common gynecological cancer in the Western World. Treatment options are limited for advanced and recurrent disease. Therefore, new treatment options are necessary. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and/or the Ras/Raf/MEK p... |
|
|
GLI inhibitor GANT-61 diminishes embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma growth by inhibiting Shh/AKT-mTOR axis.
Oncotarget 5(23) , 12151-65, (2015) Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) typically arises from skeletal muscle. Currently, RMS in patients with recurrent and metastatic disease have no successful treatment. The molecular pathogenesis of RMS varies based on cancer sub-types. Some embryonal RMS but not other s... |
|
|
The anti-diabetic drug metformin reduces BACE1 protein level by interfering with the MID1 complex.
PLoS ONE 9(7) , e102420, (2014) Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common form of dementia in the elderly, is characterized by two neuropathological hallmarks: senile plaques, which are composed of Aβ peptides, and neurofibrillary tangles, which are composed of hyperphosphorylated TAU prote... |
|
|
The Akt-mTOR axis is a pivotal regulator of eccentric hypertrophy during volume overload.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 15881, (2015) The heart has two major modalities of hypertrophy in response to hemodynamic loads: concentric and eccentric hypertrophy caused by pressure and volume overload (VO), respectively. However, the molecular mechanism of eccentric hypertrophy remains poorly unders... |
|
|
CCI-779 (Temsirolimus) exhibits increased anti-tumor activity in low EGFR expressing HNSCC cell lines and is effective in cells with acquired resistance to cisplatin or cetuximab.
J. Transl. Med. 13 , 106, (2015) The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in numerous cellular processes involving growth, proliferation and survival. The purpose of this study was to investigate the anti-tumoral effect of the mTOR inhibitor (mTORi) CCI... |
|
|
Phosphorylation-independent mTORC1 inhibition by the autophagy inducer Rottlerin.
Cancer Lett. 360(1) , 17-27, (2015) We recently found that Rottlerin not only inhibits proliferation but also causes Bcl-2- and Beclin 1-independent autophagic death in apoptosis-resistant breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells. Having excluded a role for canonical signaling pathways, the current st... |
|
|
Rapamycin ester analog CCI-779/Temsirolimus alleviates tau pathology and improves motor deficit in mutant tau transgenic mice.
J. Alzheimers Dis. 44(4) , 1145-56, (2015) Neurofibrillary tangles are intracellular inclusions made of tau protein that accumulates in neurons in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and in other tauopathies. We have investigated the ability of the rapamycin ester CCI-779/Temsilorimus, a mTOR inhibitor with bett... |
|
|
mTOR inhibitors induce cell-cycle arrest and inhibit tumor growth in Epstein-Barr virus-associated T and natural killer cell lymphoma cells.
Clin. Cancer Res. 20(21) , 5412-22, (2014) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects B cells, as well as T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, and is associated with T or NK cell lymphoid malignancies. In various tumor cells, mTOR performs an essential function together with Akt with regard to cell growth. We... |