| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
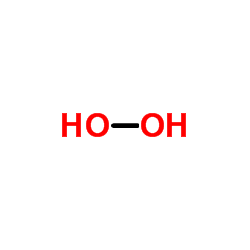 |
过氧化氢
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
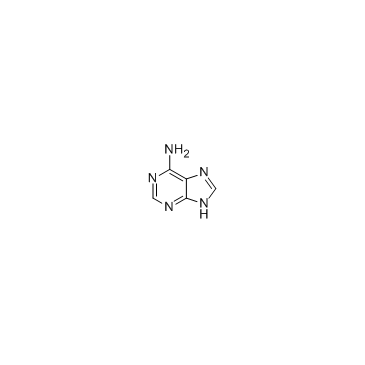 |
腺嘌呤
CAS:73-24-5 |
|
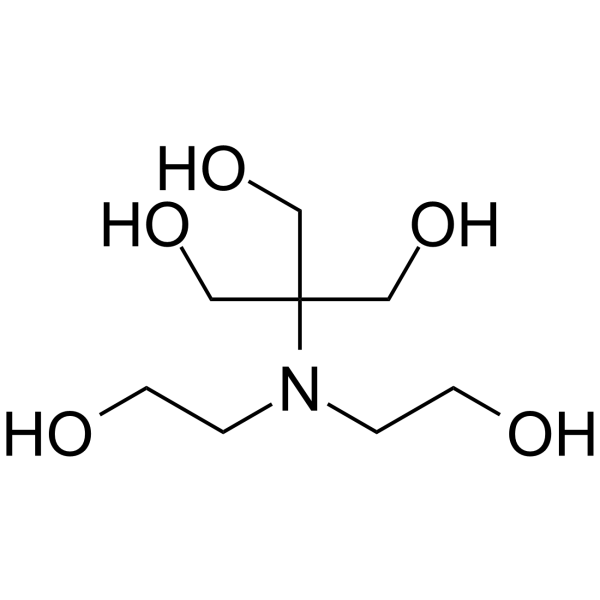 |
二(2-羟乙基)亚氨基三(羟甲基)甲烷
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
 |
L-谷氨酰胺
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
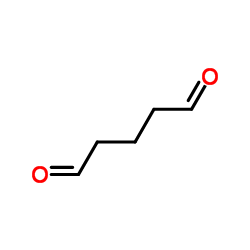 |
戊二醛
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
 |
N,N,N',N'-四甲基对苯二胺 二盐酸盐
CAS:637-01-4 |
|
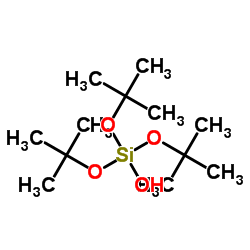 |
三(叔丁氧基)硅烷醇
CAS:18166-43-3 |
|
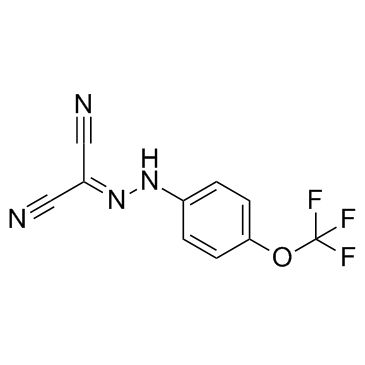 |
碳酰氰-4-三氟甲氧基苯腙
CAS:370-86-5 |
|
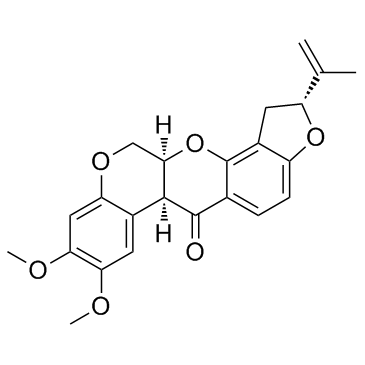 |
鱼藤酮
CAS:83-79-4 |
|
 |
吗啉乙磺酸
CAS:4432-31-9 |