| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氟化氢
CAS:7664-39-3 |
|
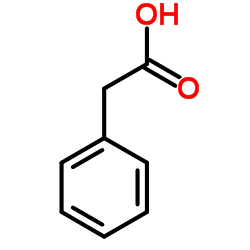 |
苯乙酸
CAS:103-82-2 |
|
 |
硅烷偶联剂KH-550
CAS:919-30-2 |
|
 |
L-谷氨酰胺
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
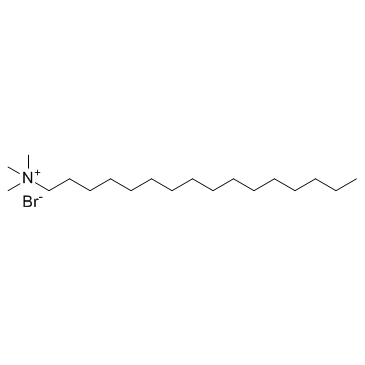 |
十六烷基三甲基溴化铵
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
 |
MES 水合物
CAS:1266615-59-1 |
|
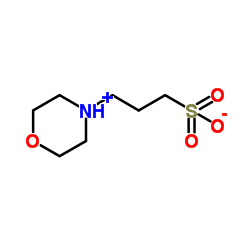 |
3-(N-吗啉)丙磺酸
CAS:1132-61-2 |
|
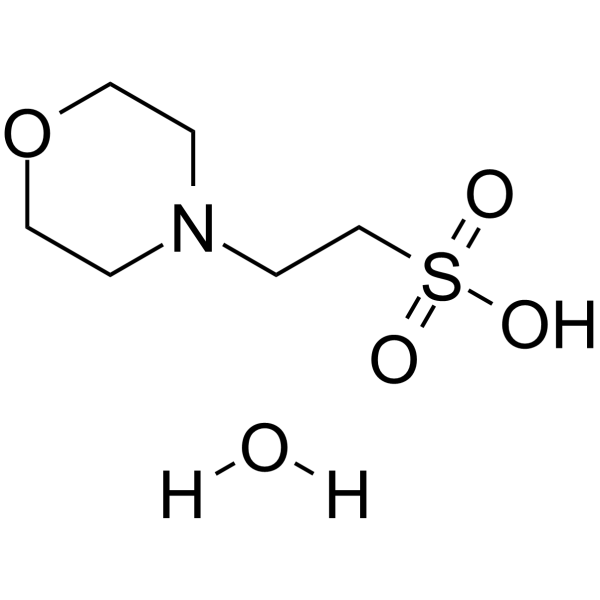 |
吗啉乙磺酸 一水合物(MES)
CAS:145224-94-8 |
|
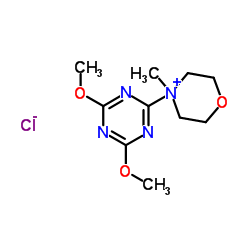 |
氯化4-(4,6-二甲氧基-1,3,5-三嗪-2-基)-4-甲基吗啉
CAS:3945-69-5 |
|
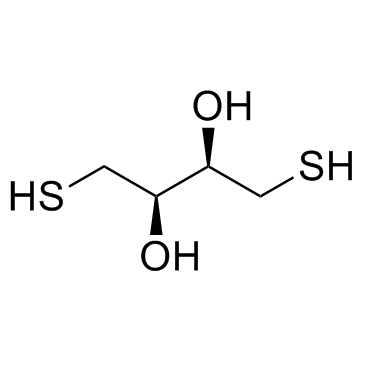 |
DL-二硫苏糖醇
CAS:3483-12-3 |