| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
环孢霉素A
CAS:59865-13-3 |
|
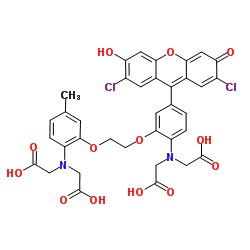 |
荧光钙探针FLUO-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
 |
N-乙酰半胱氨酸
CAS:616-91-1 |
|
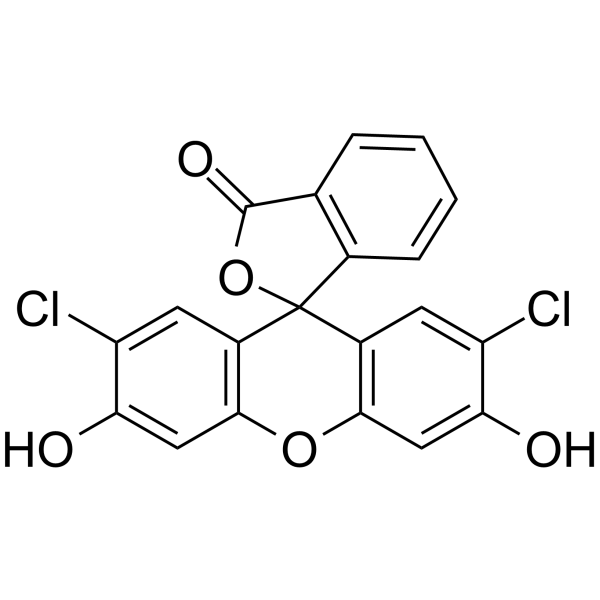 |
2',7'-二氯荧光素
CAS:76-54-0 |
|
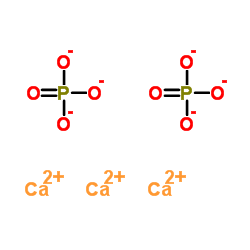 |
磷酸三钙
CAS:7758-87-4 |
|
 |
4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚二盐酸盐
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
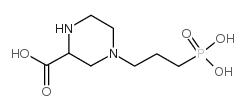 |
4-(3-膦酰基丙基)哌嗪-2-羧酸
CAS:100828-16-8 |
|
 |
噻唑兰
CAS:298-93-1 |
|
 |
argon-40
CAS:1290046-39-7 |