| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
环孢霉素A
CAS:59865-13-3 |
|
 |
咖啡因
CAS:58-08-2 |
|
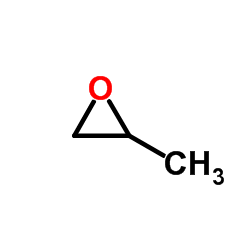 |
环氧丙烷
CAS:75-56-9 |
|
 |
明胶
CAS:9000-70-8 |
|
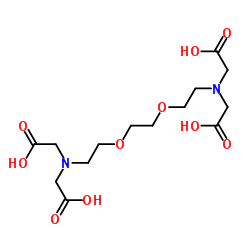 |
3,6-二氧杂-1,8-辛二胺四乙酸(EGTA)
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
 |
钌
CAS:7440-18-8 |
|
 |
四甲基罗丹明甲酯高氯酸盐
CAS:115532-50-8 |
|
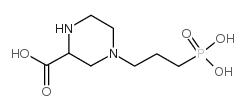 |
4-(3-膦酰基丙基)哌嗪-2-羧酸
CAS:100828-16-8 |