b-Resorcylaldehyde
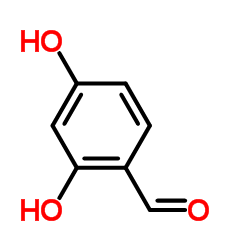
b-Resorcylaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | b-Resorcylaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 95-01-2 | Molecular Weight | 138.121 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 350.7±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 | Melting Point | 135-137 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 165.9±16.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of b-Resorcylaldehyde2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde is an endogenous metabolite. |
| Name | 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 350.7±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 135-137 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 138.121 |
| Flash Point | 165.9±16.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 138.031693 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 1.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.674 |
| InChIKey | IUNJCFABHJZSKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=Cc1ccc(O)cc1O |
| Storage condition | -20?C Freezer |
| Stability | Stable. May be air sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VH3600000 |
| Packaging Group | I; II; III |
| HS Code | 29124900 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2912499000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2912499000. other aldehyde-ethers, aldehyde-phenols and aldehydes with other oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:9.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid, and their derivatives as phenoloxidase inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 2006-15, (2007) Phenoloxidase (PO), also known as tyrosinase, is a key enzyme in insect development, responsible for catalyzing the hydroxylation of tyrosine into o-diphenols and the oxidation of o-diphenols into o-q... |
|
|
Mining biologically-active molecules for inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH): Identification of phenmedipham and amperozide as FAAH inhibitors
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6793-6, (2009) The screening of known medicinal agents against new biological targets has been shown to be a valuable approach for revealing new pharmacology of marketed compounds. Recently, carbamate, urea and keto... |
|
|
Two-photon uncaging with the efficient 3,5-dibromo-2,4-dihydroxycinnamic caging group.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 46(14) , 2467-9, (2007)
|
| 2,4,6-TRIPHENYL-S-TRIAZINE |
| Benzaldehyde, 2,4-dihydroxy- |
| 4-Hydroxysalicylaldehyde |
| resorcialdehyde |
| 2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde |
| β-Resorcylaldehyde |
| 4-Formylresorcinol |
| MFCD00011686 |
| ethyl 7-hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylate |
| b-Resorcylaldehyde |
| Benzaldehyde,2,4-dihydroxy |
| p-hydroxysalicylic aldehyde |
| EINECS 202-383-1 |
| 2,4-dihydroxy-benzaldehyde |
 CAS#:67-66-3
CAS#:67-66-3 CAS#:108-46-3
CAS#:108-46-3 CAS#:68-12-2
CAS#:68-12-2 CAS#:41777-08-6
CAS#:41777-08-6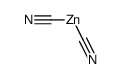 CAS#:557-21-1
CAS#:557-21-1 CAS#:103-70-8
CAS#:103-70-8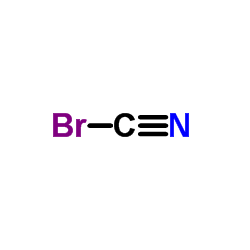 CAS#:506-68-3
CAS#:506-68-3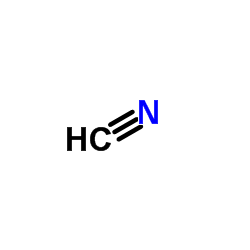 CAS#:74-90-8
CAS#:74-90-8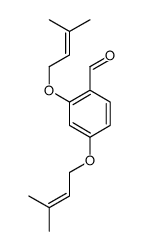 CAS#:62417-02-1
CAS#:62417-02-1 CAS#:673-22-3
CAS#:673-22-3 CAS#:54287-99-9
CAS#:54287-99-9 CAS#:33279-69-5
CAS#:33279-69-5 CAS#:496-73-1
CAS#:496-73-1 CAS#:486-21-5
CAS#:486-21-5 CAS#:533-73-3
CAS#:533-73-3 CAS#:58026-14-5
CAS#:58026-14-5![2-[(2-hydroxy-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methylamino]acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/408/141479-56-3.png) CAS#:141479-56-3
CAS#:141479-56-3 CAS#:14882-94-1
CAS#:14882-94-1 CAS#:485-72-3
CAS#:485-72-3 CAS#:4460-86-0
CAS#:4460-86-0
