2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde
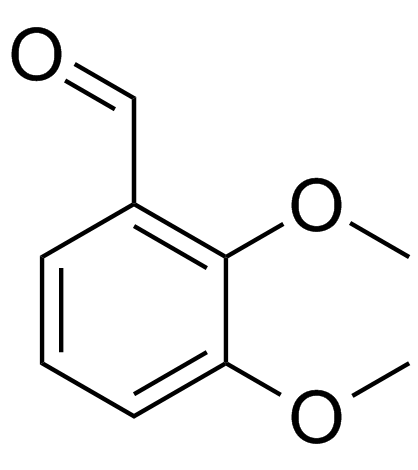
2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 86-51-1 | Molecular Weight | 166.174 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 266.7±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 | Melting Point | 48-52 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 105.8±8.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde (o-Veratraldehyde) is a benzaldehyde analog, with high antifungal activity (MIC=2.5 mM) 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde (o-Veratraldehyde) could be used for the synthesis of berberine[1]. |
| Name | 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde (o-Veratraldehyde) is a benzaldehyde analog, with high antifungal activity (MIC=2.5 mM) 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde (o-Veratraldehyde) could be used for the synthesis of berberine[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 266.7±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 48-52 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 166.174 |
| Flash Point | 105.8±8.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 166.062988 |
| PSA | 35.53000 |
| LogP | 1.63 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.534 |
| InChIKey | JIVGSHFYXPRRSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cccc(C=O)c1OC |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CU5732000 |
| HS Code | 29124900 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2912499000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2912499000. other aldehyde-ethers, aldehyde-phenols and aldehydes with other oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:9.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Antifungal activity of redox-active benzaldehydes that target cellular antioxidation.
Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 10 , 23, (2011) Disruption of cellular antioxidation systems should be an effective method for control of fungal pathogens. Such disruption can be achieved with redox-active compounds. Natural phenolic compounds can ... |
|
|
Engineering Klebsiella sp. 601 multicopper oxidase enhances the catalytic efficiency towards phenolic substrates.
BMC Biochem. 12 , 30, (2011) Structural comparison between bacterial CueO and fungal laccases has suggested that a charged residue Glu (E106) in CueO replaces the corresponding residue Phe in fungal laccases at the gate of the tu... |
| 4-Diethoxybenzene |
| Orthoveratraldehyde |
| MFCD00003309 |
| 3-DiMethoxybenzaldehyde |
| 2-VERATRALDEHYDE |
| 2,3-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde |
| 2,3-Dimethoxybenzald |
| EINECS 201-677-7 |
| Benzaldehyde, 2,3-dimethoxy- |
| dimethoxybenzaldehyde |
| 2,3-dimethoxyphenylaldehyde |
| 2,3-dimethoxtbenzaldehyde |
| O-VERATRIC ALDEHYDE |
| O-VERATRALDEHYDE |
| 2,3-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde |
| 2,3-dimethyoxybenzaldehyde |
| 2,3-dimethoxylbenzaldehyde |
 CAS#:148-53-8
CAS#:148-53-8 CAS#:74-88-4
CAS#:74-88-4 CAS#:5653-67-8
CAS#:5653-67-8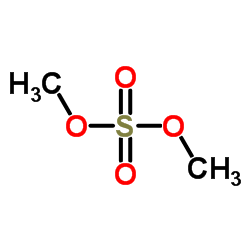 CAS#:77-78-1
CAS#:77-78-1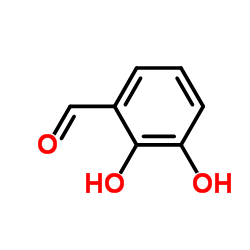 CAS#:24677-78-9
CAS#:24677-78-9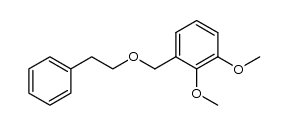 CAS#:121336-26-3
CAS#:121336-26-3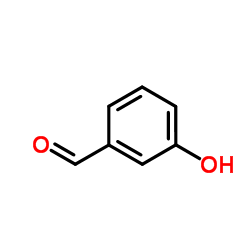 CAS#:100-83-4
CAS#:100-83-4 CAS#:492-88-6
CAS#:492-88-6 CAS#:7169-06-4
CAS#:7169-06-4 CAS#:107290-27-7
CAS#:107290-27-7 CAS#:3486-67-7
CAS#:3486-67-7![Benzo[d][1,3]dioxole-4-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/078/5768-39-8.png) CAS#:5768-39-8
CAS#:5768-39-8 CAS#:37630-20-9
CAS#:37630-20-9 CAS#:5653-62-3
CAS#:5653-62-3 CAS#:483-15-8
CAS#:483-15-8 CAS#:1521-38-6
CAS#:1521-38-6 CAS#:7461-60-1
CAS#:7461-60-1 CAS#:5470-95-1
CAS#:5470-95-1
