Cetirizine Dihydrochloride

Cetirizine Dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Cetirizine Dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 83881-52-1 | Molecular Weight | 461.81 | |
| Density | 1.237 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 542.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H27Cl3N2O3 | Melting Point | 110-115ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 281.6ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Cetirizine DihydrochlorideCetirizine 2Hcl, a second-generation antihistamine, is a major metabolite of hydroxyzine, and a racemic selective H1 receptor inverse agonist used in the treatment of allergies, hay fever, angioedema, and urticaria. IC50 value:Target: Histamine H1 receptorCetirizine crosses the blood-brain barrier only slightly, reducing the sedative side-effect common with older antihistamines. It has also been shown to inhibit eosinophil chemotaxis and LTB4 release. At a dosage of 20 mg, Boone et al. found that it inhibited the expression of VCAM-1 in patients with atopic dermatitis. The levorotary enantiomer of cetirizine, known as levocetirizine, is the more active form. From Wikipedia. |
| Name | Cetirizine Dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cetirizine 2Hcl, a second-generation antihistamine, is a major metabolite of hydroxyzine, and a racemic selective H1 receptor inverse agonist used in the treatment of allergies, hay fever, angioedema, and urticaria. IC50 value:Target: Histamine H1 receptorCetirizine crosses the blood-brain barrier only slightly, reducing the sedative side-effect common with older antihistamines. It has also been shown to inhibit eosinophil chemotaxis and LTB4 release. At a dosage of 20 mg, Boone et al. found that it inhibited the expression of VCAM-1 in patients with atopic dermatitis. The levorotary enantiomer of cetirizine, known as levocetirizine, is the more active form. From Wikipedia. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.237 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 542.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 110-115ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C21H27Cl3N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 461.81 |
| Flash Point | 281.6ºC |
| PSA | 53.01000 |
| LogP | 3.82600 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AG0977500 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2933599090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 2933599090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933599090. other compounds containing a pyrimidine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) or piperazine ring in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Involvement of the H1 Histamine Receptor, p38 MAP Kinase, Myosin Light Chains Kinase, and Rho/ROCK in Histamine-Induced Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction.
Microcirculation 22 , 237-48, (2015) The mechanisms by which histamine increases microvascular permeability remain poorly understood. We tested the hypothesis that H1 receptor activation disrupts the endothelial barrier and investigated ... |
|
|
Kinetics of the esterification of active pharmaceutical ingredients containing carboxylic acid functionality in polyethylene glycol: formulation implications.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(8) , 2424-33, (2014) Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) are attractive as excipients in the manufacture of drug products because they are water soluble and poorly immunogenic. They are used in various pharmaceutical preparations... |
|
|
Histamine H4 and H1 receptors contribute to postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity.
Gut 63(12) , 1873-82, (2014) Substantial evidence implicates mast cells and their main constituent histamine in the pathogenesis of visceral hypersensitivity. We explored the specific contribution of histamine H4 (H4R) and H1 (H1... |
| 2-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)-phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]acetic acid,dihydrochloride |
| Acetic acid, 2-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethoxy]-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| acide (2-{4-[(4-chlorophényl)(phényl)méthyl]pipérazin-1-yl}éthoxy)acétique dichlorhydrate |
| Zirtek |
| acetic acid, [2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethoxy]-, dihydrochloride |
| EINECS 222-225-5 |
| MFCD00941428 |
| (2-{4-[(4-Chlorphenyl)(phenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)essigsäuredihydrochlorid |
| (2-{4-[(4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methyl]-1-piperazinyl}ethoxy)acetic acid dihydrochloride |
| (2-{4-[(4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)acetic acid dihydrochloride |
| Zyrlex |
| cetirizine dihydrochloride |
| Cetirizine (dihydrochloride) |
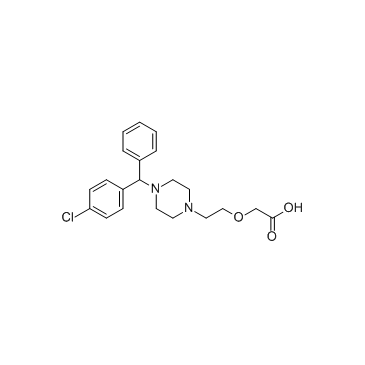 CAS#:83881-51-0
CAS#:83881-51-0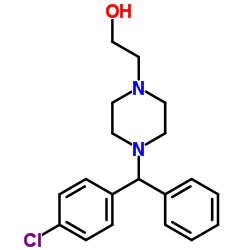 CAS#:109806-71-5
CAS#:109806-71-5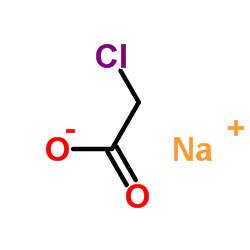 CAS#:3926-62-3
CAS#:3926-62-3 CAS#:83881-37-2
CAS#:83881-37-2![(RS)-N,N-diethyl-{2-[4-(α-phenyl-p-chloro-benzyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy}-acetamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/252/343781-29-3.png) CAS#:343781-29-3
CAS#:343781-29-3![(RS)-N,N-diallyl-{2-[4-(α-phenyl-p-chloro-benzyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy}-acetamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/397/343781-30-6.png) CAS#:343781-30-6
CAS#:343781-30-6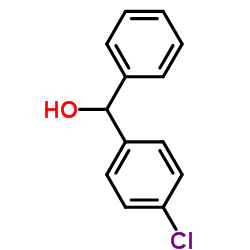 CAS#:119-56-2
CAS#:119-56-2 CAS#:134-83-8
CAS#:134-83-8 CAS#:134-85-0
CAS#:134-85-0 CAS#:83881-46-3
CAS#:83881-46-3
