4-Hydroxybenzonitrile
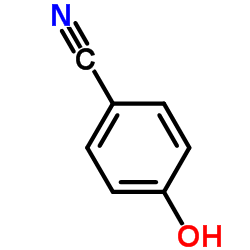
4-Hydroxybenzonitrile structure
|
Common Name | 4-Hydroxybenzonitrile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 767-00-0 | Molecular Weight | 119.121 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 281.2±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5NO | Melting Point | 110-113 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 123.9±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 4-cyanophenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 281.2±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 110-113 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5NO |
| Molecular Weight | 119.121 |
| Flash Point | 123.9±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 119.037117 |
| PSA | 44.02000 |
| LogP | 1.60 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.591 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S45-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DI4375000 |
| Packaging Group | I; II; III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29269095 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2926909090 other nitrile-function compounds VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm... |
|
|
Formation of trichloronitromethane and dichloroacetonitrile in natural waters: precursor characterization, kinetics and interpretation.
J. Hazard. Mater. 283 , 218-26, (2014) During the chloramination of natural waters, both chloramines and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) can serve as nitrogen sources for the formation of trichloronitromethane (TCNM) and dichloroacetonitr... |
|
|
Tuning the basicity of cyano-containing ionic liquids to improve SO2 capture through cyano-sulfur interactions.
Chemistry 21(14) , 5632-9, (2015) A new approach has been developed to improve SO2 sorption by cyano-containing ionic liquids (ILs) through tuning the basicity of ILs and cyano-sulfur interaction. Several kinds of cyano-containing ILs... |
| para-hydroxybenzonitrile |
| p-hydroxybenzoic hydrazide |
| 4-Cyanophenol |
| 4-hydroxybenzhydrazide |
| Benzonitrile, 4-hydroxy- |
| p-Hydroxybenzhydrazide |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide |
| p-Hydroxybenzonitrile |
| p-hydroxybenzoylhydrazine |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide |
| 4-Hydroxybenzonitrile |
| EINECS 212-175-2 |
| MFCD00002312 |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic hydrazide |
| P-CYANOPHENOL |
| 4-hydroxybenzoylhydrazine |
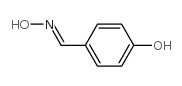 CAS#:699-06-9
CAS#:699-06-9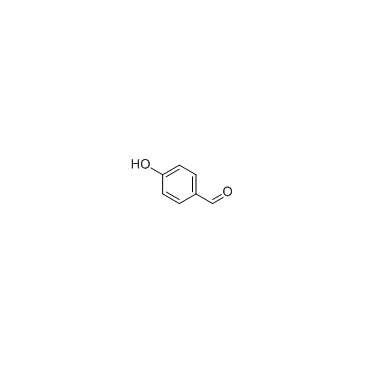 CAS#:123-08-0
CAS#:123-08-0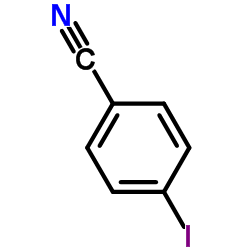 CAS#:3058-39-7
CAS#:3058-39-7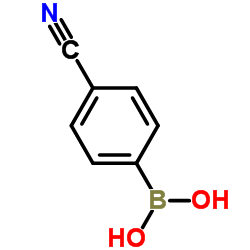 CAS#:126747-14-6
CAS#:126747-14-6 CAS#:38148-63-9
CAS#:38148-63-9 CAS#:33148-47-9
CAS#:33148-47-9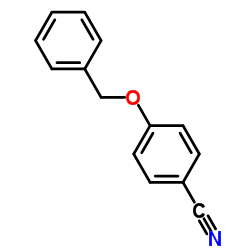 CAS#:52805-36-4
CAS#:52805-36-4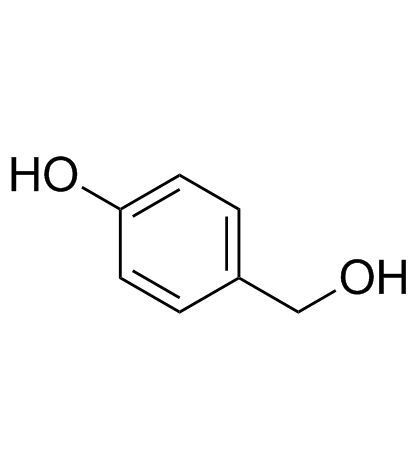 CAS#:623-05-2
CAS#:623-05-2 CAS#:71597-85-8
CAS#:71597-85-8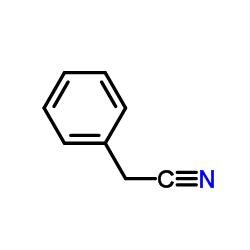 CAS#:140-29-4
CAS#:140-29-4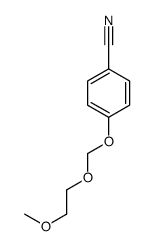 CAS#:104575-17-9
CAS#:104575-17-9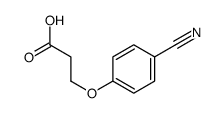 CAS#:58228-89-0
CAS#:58228-89-0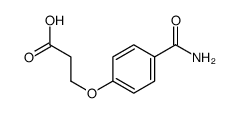 CAS#:111140-92-2
CAS#:111140-92-2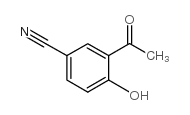 CAS#:35794-84-4
CAS#:35794-84-4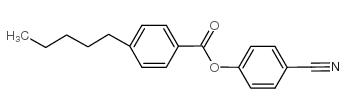 CAS#:49763-64-6
CAS#:49763-64-6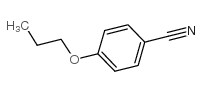 CAS#:60758-84-1
CAS#:60758-84-1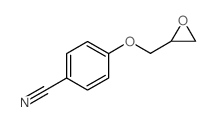 CAS#:38791-92-3
CAS#:38791-92-3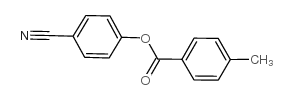 CAS#:32792-42-0
CAS#:32792-42-0
