Hippuryl-Phe-OH

Hippuryl-Phe-OH structure
|
Common Name | Hippuryl-Phe-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 744-59-2 | Molecular Weight | 326.346 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 673.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N2O4 | Melting Point | 140-144ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 361.0±31.5 °C | |
Use of Hippuryl-Phe-OHHippuryl-L-phenylalanine is a substrate of carboxypeptidase. Carboxypeptidase is a protease enzyme that related with obesity, epilepsy and neurodegeneration. Hippuryl-L-phenylalanine can be used for the determination of carboxypeptidase activity[1][2]. |
| Name | n-benzoyl-gly-phe |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hippuryl-L-phenylalanine is a substrate of carboxypeptidase. Carboxypeptidase is a protease enzyme that related with obesity, epilepsy and neurodegeneration. Hippuryl-L-phenylalanine can be used for the determination of carboxypeptidase activity[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 673.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 140-144ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 326.346 |
| Flash Point | 361.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 326.126648 |
| PSA | 95.50000 |
| LogP | 2.18 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.600 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|
~75% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: Litvinenko, L. M.; Kosmynin, V. V.; Kaida, L. N.; Savelova, V. A.; Verbovaya, I. P. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1986 , vol. 22, # 4 p. 784 - 785 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1986 , vol. 22, # 4 p. 877 - 878 |
|
~69% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: Chung-hsi, Li; Yuen-hwa, Yieh; Yao, Lin; Yong-jun, Lu; Ai-hsueh, Chi; Chi-yi, Hsing Tetrahedron Letters, 1981 , vol. 22, # 36 p. 3467 - 3470 |
|
~% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 22, # 36 p. 3467 - 3470 |
|
~% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 22, # 36 p. 3467 - 3470 |
|
~% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 22, # 36 p. 3467 - 3470 |
|
~% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: J. Gen. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 39, # 1 p. 92 - 96,81 - 83 |
|
~% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: J. Gen. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 39, # 1 p. 92 - 96,81 - 83 |
|
~% 
Hippuryl-Phe-OH CAS#:744-59-2 |
| Literature: J. Gen. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 39, # 1 p. 92 - 96,81 - 83 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Structural and functional characterization of ochratoxinase, a novel mycotoxin-degrading enzyme.
Biochem. J. 462(3) , 441-52, (2014) Ochratoxin, with ochratoxin A as the dominant form, is one of the five major mycotoxins most harmful to humans and animals. It is produced by Aspergillus and Penicillium species and occurs in a wide r... |
|
|
Mast cell proteases.
Meth. Enzymol. 80 , 588, (1981)
|
|
|
Mechanisms for activation and inhibition of carboxypeptidase A catalyzed hydrolyses of peptides and esters.
Can. J. Biochem. 56 , 329, (1978) 3,3-Diphenylpropanoate (DPP) activates the carboxypeptidase A catalyzed hydrolysis of benzoylglycyl-L-phenylalanine (BzGly-L-Phe) (Ka = 2.1 x 10 (-3) M) and inhibits ester hydrolysis uncompetitively (... |
| HIPPURYL-PHE-OH |
| BENZOYL-GLY-L-PHE |
| MFCD00037265 |
| HIPPURYL-L-PHE |
| HIPP-L-PHE |
| Einecs 212-016-7 |
| hippurylphenylalanine |
| L-Phenylalanine, N-benzoylglycyl- |
| hippuryl-L-phenylalanine |
| BENZOYL-GLY-PHE |
| HIPPURYL-PHE |
| BZ-GLY-PHE-OH |
| N-Benzoylglycyl-L-phenylalanine |

![N-[2-Oxo-2-(2-thioxo-3-thiazolidinyl)ethyl]benzamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/236/80681-03-4.png)

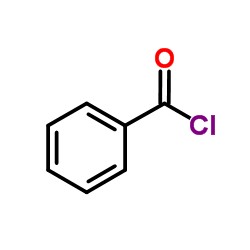
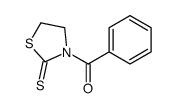

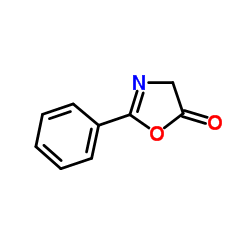
 CAS#:150-30-1
CAS#:150-30-1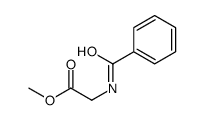 CAS#:1205-08-9
CAS#:1205-08-9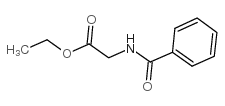 CAS#:1499-53-2
CAS#:1499-53-2
