Ranitidine S-Oxide
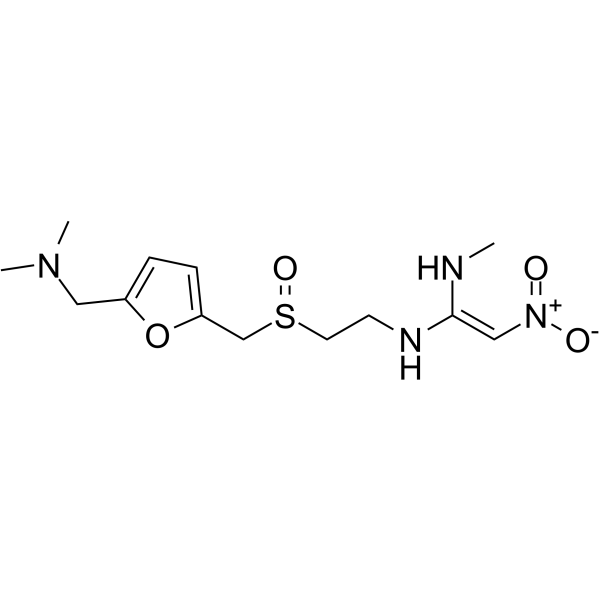
Ranitidine S-Oxide structure
|
Common Name | Ranitidine S-Oxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73851-70-4 | Molecular Weight | 330.40300 | |
| Density | 1.265g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H22N4O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 272.8ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Ranitidine S-OxideRanitidine S-oxide is the metabolite of Ranitidine (HY-B0693). Ranitidine is a potent, selective and orally active histamine H2-receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 3.3 μM that inhibits gastric secretion[1][2]. |
| Name | Ranitidine S-Oxide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ranitidine S-oxide is the metabolite of Ranitidine (HY-B0693). Ranitidine is a potent, selective and orally active histamine H2-receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 3.3 μM that inhibits gastric secretion[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.265g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 527.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H22N4O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 330.40300 |
| Flash Point | 272.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 330.13600 |
| PSA | 122.54000 |
| LogP | 2.64520 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.577 |
| Storage condition | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 37-42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Phenotypes of flavin-containing monooxygenase activity determined by ranitidine N-oxidation are positively correlated with genotypes of linked FM03 gene mutations in a Korean population.
Pharmacogenetics 10(1) , 67-78, (2000) A non-invasive urine analysis method to determine the in-vivo flavin-containing mono-oxygenase (FMO) activity catalysing N-oxidation of ranitidine (RA) was developed and used to phenotype a Korean pop... |
|
|
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of ranitidine and its metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 323(1) , 143-52, (1985) Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography systems for the separation of ranitidine and its metabolites ranitidine-N-oxide, ranitidine-S-oxide, and desmethylranitidine have been developed f... |
|
|
Sulphoxidation and sulphation capacity in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis.
J. Hepatol. 22(5) , 551-60, (1995) We have previously reported an association of impaired S-oxidation with primary biliary cirrhosis. In order to confirm and further define this relationship, we retested S-oxidation capacity via three ... |
| (E)-1-N'-[2-[[5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl]methylsulfinyl]ethyl]-1-N-methyl-2-nitroethene-1,1-diamine |
| Ranitidine Impurity 3 |