Atractylenolide III
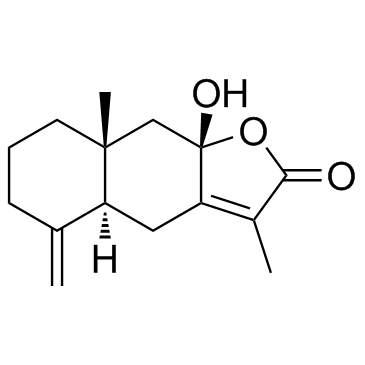
Atractylenolide III structure
|
Common Name | Atractylenolide III | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73030-71-4 | Molecular Weight | 248.318 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 424.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O3 | Melting Point | 200-201ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 181.1±21.5 °C | |
Use of Atractylenolide IIIAtractylenolide III is a major component of Atractylodes rhizome can induce apoptosis of the lung carcinoma cells.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: ATL-III inhibited cell growth, increased lactate dehydrogenase release and modulated cell cycle on human lung carcinoma A549 cells. ALT-III induced the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 and cleavage of poly-(ADP)-ribose polymerase. ATL-III induced the release of cytochrome c, upregulation of bax expression, and translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor [1]. Atractylenolide II did not show cytoprotective effects, but oral administration of atractylenolide III dose-dependently prevented ethanol-induced PRGM cell death and cell membrane damage. The EC50 values were 0.27 and 0.34 mm, respectively [2]. Against adult D. pteronyssinus, atractylenolide III (LD50, 73.8 mg/m2) and atractylon (72.1 mg/m2) were eight times more active than Deet and 2.5-fold more toxic than dibutyl phthalate [3].in vivo: In the in-vivo assay, atractylenolide III 10 mg/kg significantly reduced 70% ethanol-induced Wistar rat gastric ulcer. Atractylenolide III could inhibit matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 expression through upregulation of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase from the gastric ulcerated tissues [2]. |
| Name | Atractylenolide III |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Atractylenolide III is a major component of Atractylodes rhizome can induce apoptosis of the lung carcinoma cells.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer natural compoundin vitro: ATL-III inhibited cell growth, increased lactate dehydrogenase release and modulated cell cycle on human lung carcinoma A549 cells. ALT-III induced the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 and cleavage of poly-(ADP)-ribose polymerase. ATL-III induced the release of cytochrome c, upregulation of bax expression, and translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor [1]. Atractylenolide II did not show cytoprotective effects, but oral administration of atractylenolide III dose-dependently prevented ethanol-induced PRGM cell death and cell membrane damage. The EC50 values were 0.27 and 0.34 mm, respectively [2]. Against adult D. pteronyssinus, atractylenolide III (LD50, 73.8 mg/m2) and atractylon (72.1 mg/m2) were eight times more active than Deet and 2.5-fold more toxic than dibutyl phthalate [3].in vivo: In the in-vivo assay, atractylenolide III 10 mg/kg significantly reduced 70% ethanol-induced Wistar rat gastric ulcer. Atractylenolide III could inhibit matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 expression through upregulation of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase from the gastric ulcerated tissues [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 424.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 200-201ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 248.318 |
| Flash Point | 181.1±21.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 248.141251 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 2.36 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | methanol: soluble1mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
Sesquiterpenoids from Atractylodes macrocephala act as farnesoid X receptor and progesterone receptor modulators.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22 , 2326-2329, (2012) Two sesquiterpenoids, atractylenolide II and III, were isolated and identified from Atractylodes macrocephala (Asteraceae) to be subsequently evaluated for their activity against farnesoid X receptor ... |
|
|
Targeting of the Sonic Hedgehog pathway by atractylenolides promotes chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35 , 1328-1335, (2012) Molecules that enhance chondrogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were identified and isolated using an in vitro Gli reporter gene assay in MSCs incorporating a Sonic Hedgehog (Shh)... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Active Ingredients and Its Metabolites Derived from Rikkunshito, a Ghrelin Enhancer, in Healthy Japanese Volunteers: A Cross-Over, Randomized Study.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0133159, (2015) Rikkunshito, a traditional Japanese (Kampo) medicine, has been used to treat upper gastrointestinal disorders such as functional dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux. This study investigated the expo... |
| Atractylenolide III |
| Naphtho(2,3-b)furan-2(4H)-one, 4a,5,6,7,8,8a,9,9a-octahydro-9a-hydroxy-3,8a-dimethyl-5-methylene-, (4aS,8aR,9aS)- |
| codonolactone |
| ATRACTYLENOLIDE |
| 8-HYDROXYASTEROLIDE |
| (4aS,8aR,9aS)-9a-Hydroxy-3,8a-dimethyl-5-methylene-4a,5,6,7,8,8a,9,9a-octahydronaphtho[2,3-b]furan-2(4H)-one |
| Naphtho[2,3-b]furan-2(4H)-one, 4a,5,6,7,8,8a,9,9a-octahydro-9a-hydroxy-3,8a-dimethyl-5-methylene-, (4aS,8aR,9aS)- |