L-Threonine
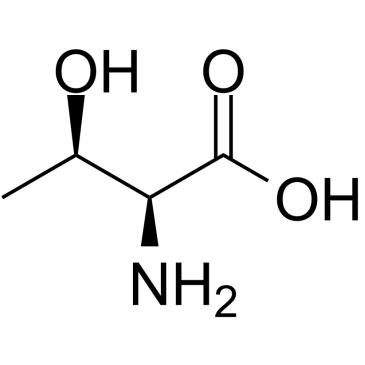
L-Threonine structure
|
Common Name | L-Threonine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 72-19-5 | Molecular Weight | 119.119 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 345.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO3 | Melting Point | 255ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 162.9±25.1 °C | |
Use of L-ThreonineL-Threonine is a natural amino acid, can be produced by microbial fermentation, and is used in food, medicine, or feed[1]. |
| Name | L-threonine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Threonine is a natural amino acid, can be produced by microbial fermentation, and is used in food, medicine, or feed[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 345.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 255ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 119.119 |
| Flash Point | 162.9±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 119.058243 |
| PSA | 83.55000 |
| LogP | -1.23 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.507 |
| InChIKey | AYFVYJQAPQTCCC-GBXIJSLDSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(O)C(N)C(=O)O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Urinary metabolic fingerprinting of mice with diet-induced metabolic derangements by parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 265-76, (2014) This study investigates the potential of a parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive GC platform (GC×2GC-MS/FID) for metabolic profiling and fingerprinting of mouse u... |
|
|
Mechanism of chemical activation of sodium chloride in the presence of amino acids.
Food Chem. 166 , 301-8, (2014) Sodium chloride has been shown to promote chlorination of glycerol during thermal processing. However, the detailed mechanism of this reaction is not well understood. Preliminary experiments have indi... |
|
|
The unique serine/threonine phosphatase from the minimal bacterium Mycoplasma synoviae: biochemical characterization and metal dependence.
J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 20(1) , 61-75, (2015) Serine/threonine protein phosphatases have been described in many pathogenic bacteria as essential enzymes involved in phosphorylation-dependent signal transduction pathways and frequently associated ... |
| EINECS 200-774-1 |
| L-Tlhreonine |
| H-THR-OH |
| L-Threonine (JP15) |
| (2S,3R)-(-)-Threonine |
| L-α-Amino-β-hydroxybutyric acid |
| L-Threonine |
| 2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid, (R-(R*,S*))- |
| UNII:TFM6DU5S6A |
| H-L-THR-OH |
| MFCD00063722 |
| THR |
| (R-(R*,S*))-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
| L-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid |
| Threonine |
| (2S,3R)-Threonine |
| [R-(R*,S*)]-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
| MFCD00064270 |
| (2S,3R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid |
| Butanoic acid, 2-amino-3-hydroxy-, (R-(R*,S*))- |
| QY1&YZVQ &&L or (2S,3R)- Form |
| (s)-threonine |
| l-threonin |
| (2S,3R)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
| l-Thr |
| Threonin |
 CAS#:4144-02-9
CAS#:4144-02-9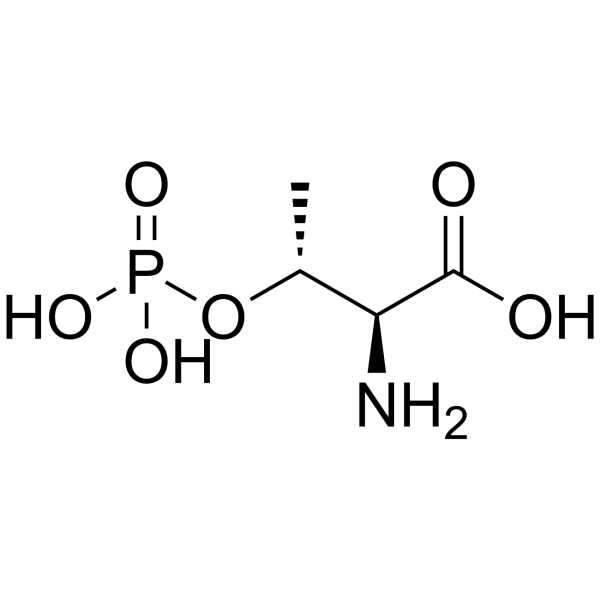 CAS#:1114-81-4
CAS#:1114-81-4 CAS#:111610-28-7
CAS#:111610-28-7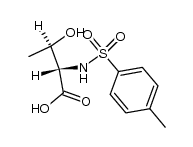 CAS#:34235-88-6
CAS#:34235-88-6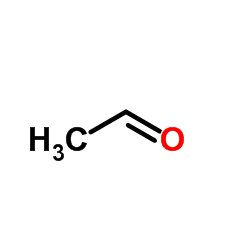 CAS#:75-07-0
CAS#:75-07-0 CAS#:7093-70-1
CAS#:7093-70-1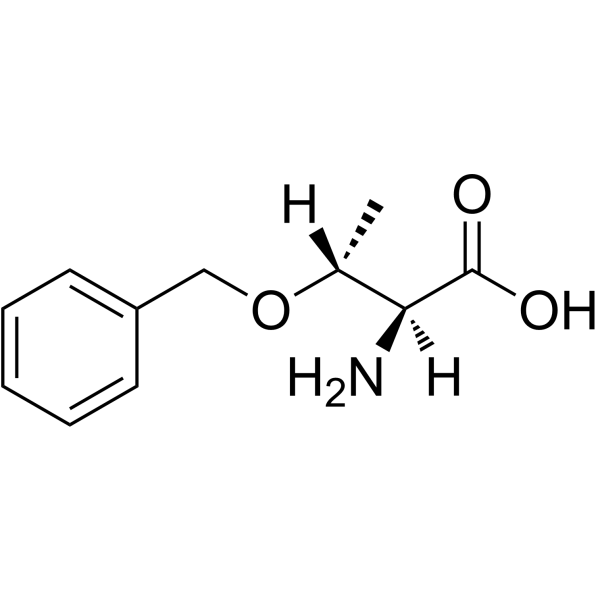 CAS#:4378-10-3
CAS#:4378-10-3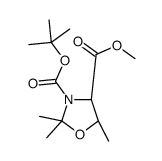 CAS#:108149-61-7
CAS#:108149-61-7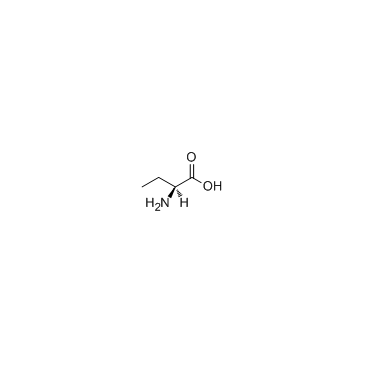 CAS#:1492-24-6
CAS#:1492-24-6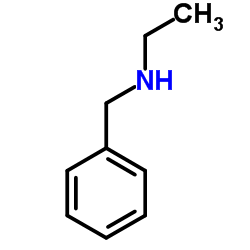 CAS#:3789-59-1
CAS#:3789-59-1 CAS#:2941-20-0
CAS#:2941-20-0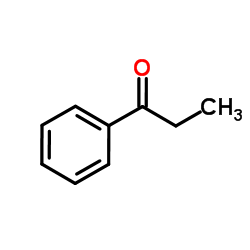 CAS#:93-55-0
CAS#:93-55-0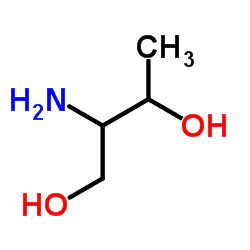 CAS#:3228-51-1
CAS#:3228-51-1 CAS#:5854-78-4
CAS#:5854-78-4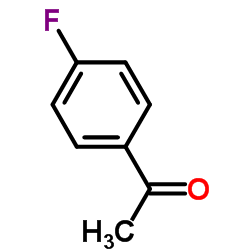 CAS#:403-42-9
CAS#:403-42-9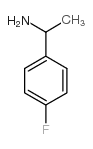 CAS#:374898-01-8
CAS#:374898-01-8 CAS#:3373-59-9
CAS#:3373-59-9
